Biology
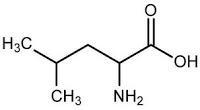 Leucine is an essential amino acid that helps to protein synthesis. It is utilized also in the liver and adipose tissue. In muscle and in adipose tissue leucine is used in the formation of sterols. It is found in foods that are high in proteins like eggs, meat, poultry and legumes.
Leucine is an essential amino acid that helps to protein synthesis. It is utilized also in the liver and adipose tissue. In muscle and in adipose tissue leucine is used in the formation of sterols. It is found in foods that are high in proteins like eggs, meat, poultry and legumes.
- Chitin
Term: chitin Literally meaning: ?pertaining to tunic?Origin: Anc Greek?????/chiton(=tunic or gown usually worn next to the skin) Coined/HistoryChitin was first isolated from mushrooms in 1811 by plant chemist Henry Braconnot (1781-1855) who originally...
- Actinium (ac)
Term: actinium (Ac)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to ray?Origin: 'á???? actis(genitive á??[é???/actinos)(=ray, beam) The element was named after its power of emitting energy in the form of rays suchas radioactive ?radium? which comes from latin...
- Asparagine (asn N)
Term: asparagin (Asn N)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to asparagus?Origin: Anc Greek??? ????????? (plant)/asparagos(asparagus) >???????/spargao(=to vigor)Coined/History Asparagine was isolated in 1806 by French chemist Louis...
- Threonine (thr T)
Term: threonine (Thr T)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to erythrose or pertaining to red?Origin: Anc Greek???????/erythros(=red)Coined/History Threonine was discovered in 1930 by American nutritionist William Cumming Rose (1887-1985) in...
- Isoleucine (ile I)
Term: isoleucineLiterally meaning: ?isomer of leucine?Origin: Anc Greek????/isos(=equal) combining form ???-/iso- eg isomer, isopod+??????/leukos(=white)Coined/History The term was coined in 1904 by German F Ehrlich who observed that in sugar there was...
Biology
leucine (Leu L)
Term: leucine
Literally meaning: ?pertaining to white?
Origin: Anc Greek
??????/leukos(=white)
Coined/History
Leucine was isolated in 1818 by French chemist Joseph Louis Proust (1754-1855) from cheese in a white crystalline state. Finally it was named by Fench chemist Henri Braconnot (1780-1855) who isolated it in a pure form from muscle.
Definition
 Leucine is an essential amino acid that helps to protein synthesis. It is utilized also in the liver and adipose tissue. In muscle and in adipose tissue leucine is used in the formation of sterols. It is found in foods that are high in proteins like eggs, meat, poultry and legumes.
Leucine is an essential amino acid that helps to protein synthesis. It is utilized also in the liver and adipose tissue. In muscle and in adipose tissue leucine is used in the formation of sterols. It is found in foods that are high in proteins like eggs, meat, poultry and legumes. - Chitin
Term: chitin Literally meaning: ?pertaining to tunic?Origin: Anc Greek?????/chiton(=tunic or gown usually worn next to the skin) Coined/HistoryChitin was first isolated from mushrooms in 1811 by plant chemist Henry Braconnot (1781-1855) who originally...
- Actinium (ac)
Term: actinium (Ac)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to ray?Origin: 'á???? actis(genitive á??[é???/actinos)(=ray, beam) The element was named after its power of emitting energy in the form of rays suchas radioactive ?radium? which comes from latin...
- Asparagine (asn N)
Term: asparagin (Asn N)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to asparagus?Origin: Anc Greek??? ????????? (plant)/asparagos(asparagus) >???????/spargao(=to vigor)Coined/History Asparagine was isolated in 1806 by French chemist Louis...
- Threonine (thr T)
Term: threonine (Thr T)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to erythrose or pertaining to red?Origin: Anc Greek???????/erythros(=red)Coined/History Threonine was discovered in 1930 by American nutritionist William Cumming Rose (1887-1985) in...
- Isoleucine (ile I)
Term: isoleucineLiterally meaning: ?isomer of leucine?Origin: Anc Greek????/isos(=equal) combining form ???-/iso- eg isomer, isopod+??????/leukos(=white)Coined/History The term was coined in 1904 by German F Ehrlich who observed that in sugar there was...
