Biology
 Source: Ehrlich, F., Ber. them. Ges., 37, 1809 (1904)
Source: Ehrlich, F., Ber. them. Ges., 37, 1809 (1904)
- Amino Acid Activation
Codons of an mRNA molecule contain genetic messages that are carried by the mRNA and they need to be translated to form the corresponding sequence of amino acids that will form the polypeptide chain and subsequently the protein. The tRNA transfers amino...
- Synthetases Use Proofreading To Improve Accuracy
KEY TERMS:Proofreading refers to any mechanism for correcting errors in protein or nucleic acid synthesis that involves scrutiny of individual units after they have been added to the chain. Kinetic proofreading describes a proofreading mechanism that...
- Related Codons Represent Related Amino Acids
KEY TERMS:Synonym codons have the same meaning in the genetic code. Synonym tRNAs bear the same amino acid and respond to the same codon. Third base degeneracy describes the lesser effect on codon meaning of the nucleotide present in the third codon...
- Isoenzyme, Isozyme
Term: isoenzyme, isozymeLiterally meaning: equal enzymes Origin: Anc Greek????/isos(=equal) combining form ???-/iso- eg isomer, isopod??????/enzymo(=enzyme) > ??/en(=in) + ????/zime(= leaven)Coined/Historyin 1959 by Markert and Moller DefinitionIsozymes...
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
Biology
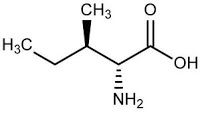
isoleucine (Ile I)
Term: isoleucine
Literally meaning: ?isomer of leucine?
Origin: Anc Greek
????/isos(=equal) combining form ???-/iso- eg isomer, isopod
+??????/leukos(=white)
Coined/History
The term was coined in 1904 by German F Ehrlich who observed that in sugar there was an amino acid very similar but not identical with leucine. Isoleucine?s constitution established 3 years later with consequent synthesis via the Strecker reaction.
 Source: Ehrlich, F., Ber. them. Ges., 37, 1809 (1904)
Source: Ehrlich, F., Ber. them. Ges., 37, 1809 (1904) Definition
Isoleucine is an essential amino acid that with valine and leucine is part of the three ?branched chain amino acids? . Isoleucine helps to muscle recovery blood-clot formation and the regulation of blood sugar levels. Nutritional sources includes eggs, soy protein turkey, chicken cheese and fish
- Amino Acid Activation
Codons of an mRNA molecule contain genetic messages that are carried by the mRNA and they need to be translated to form the corresponding sequence of amino acids that will form the polypeptide chain and subsequently the protein. The tRNA transfers amino...
- Synthetases Use Proofreading To Improve Accuracy
KEY TERMS:Proofreading refers to any mechanism for correcting errors in protein or nucleic acid synthesis that involves scrutiny of individual units after they have been added to the chain. Kinetic proofreading describes a proofreading mechanism that...
- Related Codons Represent Related Amino Acids
KEY TERMS:Synonym codons have the same meaning in the genetic code. Synonym tRNAs bear the same amino acid and respond to the same codon. Third base degeneracy describes the lesser effect on codon meaning of the nucleotide present in the third codon...
- Isoenzyme, Isozyme
Term: isoenzyme, isozymeLiterally meaning: equal enzymes Origin: Anc Greek????/isos(=equal) combining form ???-/iso- eg isomer, isopod??????/enzymo(=enzyme) > ??/en(=in) + ????/zime(= leaven)Coined/Historyin 1959 by Markert and Moller DefinitionIsozymes...
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
