Biology
 Definition
Definition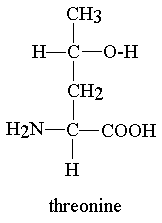 Threonine is an essential amino acid that helps for protein balance in the body, gut integrity and immunity by aiding in production of antibodies. It is needed for gycine and serine formation which are required for collagen production. Threonine is mostly found in the central nervous system. It is found in foods such as cottage cheese, poultry, lentils, fish, meat and sesame seeds.
Threonine is an essential amino acid that helps for protein balance in the body, gut integrity and immunity by aiding in production of antibodies. It is needed for gycine and serine formation which are required for collagen production. Threonine is mostly found in the central nervous system. It is found in foods such as cottage cheese, poultry, lentils, fish, meat and sesame seeds.
- Taurine
Term: taurineLiterally meaning: ?pertaining to bull?Origin: Anc Greek??????/taurus (=bull, ox)Coined/History Taurine isolated in 1827 by German Friedrich Triedemann (1781-18861) and Leopold Gmelin (1788-1853) who isolated it from ox...
- Tryptophan (trp W)
Term: tryptophan (Trp W)Literally meaning: ?to be broken and to appear?Origin: Anc Greek?????/trivo (=to rub, to powder, to grind) > (simple past) ??????/etrips? >????/tryo(=to puncture)?????/pheno(=be visible, or obvious, show)Coined/History ...
- Methionine (met M)
Term: methionine (Met M)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to methyl and sulfur?Origin: Anc Greek????/methy(=drunkenness) + ???/hely (= trunk, wood) +????/thio(=pertaining to god as it was used in worship)Coined/History Methionine, although had discovered...
- Leucine (leu L)
Term: leucineLiterally meaning: ?pertaining to white?Origin: Anc Greek??????/leukos(=white)Coined/History Leucine was isolated in 1818 by French chemist Joseph Louis Proust (1754-1855) from cheese in a white crystalline state. Finally it...
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
Biology
threonine (Thr T)
Term: threonine (Thr T)
Literally meaning: ?pertaining to erythrose or pertaining to red?
Origin: Anc Greek
???????/erythros(=red)
Coined/History
Threonine was discovered in 1930 by American nutritionist William Cumming Rose (1887-1985) in Illinois University. Its name derived by the similarity with monosacharite threose (C4H8O4) an isomer of D-erythrose. Erythrose's name derived by erythrin-erythritol which isolated from red lichens.
 Definition
Definition Threonine is an essential amino acid that helps for protein balance in the body, gut integrity and immunity by aiding in production of antibodies. It is needed for gycine and serine formation which are required for collagen production. Threonine is mostly found in the central nervous system. It is found in foods such as cottage cheese, poultry, lentils, fish, meat and sesame seeds.
Threonine is an essential amino acid that helps for protein balance in the body, gut integrity and immunity by aiding in production of antibodies. It is needed for gycine and serine formation which are required for collagen production. Threonine is mostly found in the central nervous system. It is found in foods such as cottage cheese, poultry, lentils, fish, meat and sesame seeds. - Taurine
Term: taurineLiterally meaning: ?pertaining to bull?Origin: Anc Greek??????/taurus (=bull, ox)Coined/History Taurine isolated in 1827 by German Friedrich Triedemann (1781-18861) and Leopold Gmelin (1788-1853) who isolated it from ox...
- Tryptophan (trp W)
Term: tryptophan (Trp W)Literally meaning: ?to be broken and to appear?Origin: Anc Greek?????/trivo (=to rub, to powder, to grind) > (simple past) ??????/etrips? >????/tryo(=to puncture)?????/pheno(=be visible, or obvious, show)Coined/History ...
- Methionine (met M)
Term: methionine (Met M)Literally meaning: ?pertaining to methyl and sulfur?Origin: Anc Greek????/methy(=drunkenness) + ???/hely (= trunk, wood) +????/thio(=pertaining to god as it was used in worship)Coined/History Methionine, although had discovered...
- Leucine (leu L)
Term: leucineLiterally meaning: ?pertaining to white?Origin: Anc Greek??????/leukos(=white)Coined/History Leucine was isolated in 1818 by French chemist Joseph Louis Proust (1754-1855) from cheese in a white crystalline state. Finally it...
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
