Biology
Students, here are the pages you need to work on.
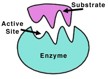
Choose ENZYMES: The BASICS
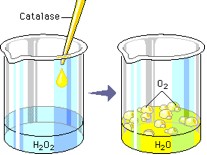 Enzyme = catalase, found in your liver
Enzyme = catalase, found in your liver
- Enzyme Inhibition
In competitive inhibition, inhibitor has a shape, charge, size and structure similar to that of the substrate. It therefore competes with the substrate for the active sites to form the enzyme-inhibitor complex (E-I complex) and reduces the number of active...
- Q: Distinguish Between Competitive And Non-competitive Inhibition Of Enzymes
A competitive inhibitor is structurally similar to the substrate but a non-competitive inhibitor is often structurally different from the substrate. Hence, a competitive inhibitor will compete with the substrate for an active site but a non competitive...
- #18. Enzymes - Active Site, Activation Energy, Enzyme Specificity
Enzymes are globular proteins that serve as biological catalysts. They speed up or slow down metabolic reaction, but remain unchanged. They may facilitate the breaking of an existing bond or the formation of a new bond....
- #17.1 Enzymes - Syllabus 2015
? Mode of action of enzymes ? Factors that affect enzyme action Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) explain that enzymes are globular proteins that catalyse metabolic reactions; (b) explain the mode of action of enzymes in terms of...
- Enzymes
ENZYMES Enzymes are biological catalysts which influence biochemical reactions. All enzymes are proteins but all proteins are not enzymes because there are proteins other than enzymes. Ribozymes: These are the Nucleic acids (RNA) that behave like...
Biology
Webquest Oct 28th, 2010
Students, here are the pages you need to work on.

ENZYME WEBQUEST
WEBSITE #1: http://www.northland.cc.mn.us/biology/Biology1111/animations/enzyme.html
Choose ENZYMES: The BASICS
1. SLIDE ONE: Enzymes are ________________that serve as __________________.
They _________________up or _______________ ______________reactions, but ALWAYS remain _________________.
2. SLIDE TWO: What is an ACTIVE SITE?
3. SLIDE THREE: Each ______________acts on a specific_____________.
4. What is a SUBSTRATE?
5. DRAW an ENZYME and SUBSTRATE below. Make each a DIFFERENT COLOR and label each.
6. SLIDE FIVE: YOU JUST DRANK A GLASS OF MILK! DRAW THE CATALYTIC CYCLE OF LACTOSE BELOW! LABELING THE SUBSTRATE, SUBSTRATE ENZYME COMPLEX, THE ACTIVE SITE, AND THE PRODUCTS. MAKING EACH A DIFFERENT COLOR!
7. Someone who is ?LACTOSE INTOLERANT??is lacking which enzyme?____________________
WEBSITE #2: http://www.phschool.com/science/biology_place/labbench/lab2/intro.html
Enzyme Catalysis
Key Concepts
8. _________________ catalyze reactions by lowering the _______________ _________________ necessary for a reaction to occur. The molecule that an enzyme acts on is called the _________________. In an enzyme-mediated reaction, _________________ molecules are changed, and _________________ is formed. The _________________molecule is _________________ after the reaction, and it can continue___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________.
9. Each _________________ is _________________for the _________________ it will catalyze. In this laboratory,

Substrate = hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)
Products = water and oxygen
10. DRAW THE REACTION THAT TOOK PLACE ON THE LEFT USING YOUR OWN SHAPES, LABELING THE SUBSTRATE, ENZYME, ACTIVE SITE ON THE ENZYME, ENZYME-SUBSTRATE COMPLEX, AND THE PRODUCTS.
Enzyme Structure
11. Enzymes are globular, functional _____________________. Their folded conformation creates an area known as the _________________ _______________. The nature and arrangement of __________________ ____________________ in the __________________ __________________ make it specific__________________________________________________________.
12. DRAW A MODEL OF AN ENZYME, ACTIVE SITE, AND SUBSTRATE BELOW:
Some Factors That Affect Enzyme Action
13. The conformation of an enzyme is maintained by interactions between the various ___________________ _______________ that compose it, and this conformation is sensitive to ________________________________________. Two important influences are _________________ and ________________. When an enzyme's ________________________ is significantly altered because of ____________ or ___________________ variation, the enzyme may no longer _____________________ ___________________. An enzyme is said to be _____________________ when it loses its functional shape.
pH and Enzyme Function
14. Each enzyme functions best within a _______________________. For example, the enzyme__________________, which works in your stomach, functions best in a strongly ____________________environment. Lipase, an enzyme found in your _____________________________, works best in a __________________ environment.
15. When the pH changes, the active site ____________________________ and affects ____________________ ________________. What happens to catalysis when an enzyme is subjected to a pH far from its optimum range?
16. WATCH THE ANIMATION AND DESCRIBE WHAT YOU SEE BELOW:
Temperature and Enzyme Function
17. Chemical reactions speed up as ____________________ is increased, so, in general,_________________ will ___________________ at higher temperatures. However, each enzyme has a temperature __________________________, and beyond this point the enzyme's _____________________________ is lost. ___________________ temperatures will ______________________ most enzymes.
WEBSITE#3
:http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp06/0602001.html
GO TO ANIMATION, then to STEP THROUGH
1st-Add a SUBSTRATE
2nd-Add an ENZYME
PRESS PLAY
18. Describe what happened:
WEBSITE #4: http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/content/chp06/0602002.html
Make sure you are in the ANIMATION portion and go to STEP THROUGH?Watch the animation?it is a bit complicated. Main idea I need you to understand is?.
19. TRUE or FALSE: an enzyme can change shape and become ACTIVE or INACTIVE.
- Enzyme Inhibition
In competitive inhibition, inhibitor has a shape, charge, size and structure similar to that of the substrate. It therefore competes with the substrate for the active sites to form the enzyme-inhibitor complex (E-I complex) and reduces the number of active...
- Q: Distinguish Between Competitive And Non-competitive Inhibition Of Enzymes
A competitive inhibitor is structurally similar to the substrate but a non-competitive inhibitor is often structurally different from the substrate. Hence, a competitive inhibitor will compete with the substrate for an active site but a non competitive...
- #18. Enzymes - Active Site, Activation Energy, Enzyme Specificity
Enzymes are globular proteins that serve as biological catalysts. They speed up or slow down metabolic reaction, but remain unchanged. They may facilitate the breaking of an existing bond or the formation of a new bond....
- #17.1 Enzymes - Syllabus 2015
? Mode of action of enzymes ? Factors that affect enzyme action Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) explain that enzymes are globular proteins that catalyse metabolic reactions; (b) explain the mode of action of enzymes in terms of...
- Enzymes
ENZYMES Enzymes are biological catalysts which influence biochemical reactions. All enzymes are proteins but all proteins are not enzymes because there are proteins other than enzymes. Ribozymes: These are the Nucleic acids (RNA) that behave like...
