Biology
- Gene Mutation
A gene mutation is a change in one or several bases. A base may be added, deleted, or substituted with another base. This is caused often through the action of damaging chemicals, radiations, or through errors inherent in DNA replication and repair reactions....
- Amino Acid Activation
Codons of an mRNA molecule contain genetic messages that are carried by the mRNA and they need to be translated to form the corresponding sequence of amino acids that will form the polypeptide chain and subsequently the protein. The tRNA transfers amino...
- Aspartate Or Aspartic Acid (asp Or D)
Term: aspartic acid (Asp or D) or L-AspartateLiterally meaning: ?pertaining to asparagine?Origin: Anc Greek??? ????????? (plant)/asparagos(asparagus) >???????(=vigor)Coined/History Asparagine was isolated in 1806 by French chemist...
- Glucose
Term: glucoseLiterally meaning: ?sweet like?Origin: Greek??????/glycos(=sweet, delightful,) as glycose, an older term for glucose .Coined/History(?)Glucose was discovered in 1747 by German chemist Andreas Marrgraf (1709-1782), who isolated it in raisins....
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
Biology
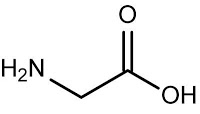
glycine (Gly C)
Term: glycine
Literally meaning: ?pertaining to sweet?
Origin: Anc Greek
??????/glykys (=sweet) >????/lyki(=pleasant, bright)
Coined/History
In 1818 the French chemist Henri Braconnot(1780-1855) isolated glycine from gelatin and named it ?sucrede gelatine? because of its sweet taste. In 1846 Eben Norton Horsford (1818-1893) named it ?glycocoll? and finally Berzalius used first the name ?glycine?
Definition

Glycine is a colourless sweet- tasting and non?essential amino acid. It is the smaller of amino acids found in human proteins. Glycine is important amino acid because it is a precursor for proteins, regulates the synthesis of bile, and as a glucogenic amino acid contributes to supply the body with glucose needed for energy.
- Gene Mutation
A gene mutation is a change in one or several bases. A base may be added, deleted, or substituted with another base. This is caused often through the action of damaging chemicals, radiations, or through errors inherent in DNA replication and repair reactions....
- Amino Acid Activation
Codons of an mRNA molecule contain genetic messages that are carried by the mRNA and they need to be translated to form the corresponding sequence of amino acids that will form the polypeptide chain and subsequently the protein. The tRNA transfers amino...
- Aspartate Or Aspartic Acid (asp Or D)
Term: aspartic acid (Asp or D) or L-AspartateLiterally meaning: ?pertaining to asparagine?Origin: Anc Greek??? ????????? (plant)/asparagos(asparagus) >???????(=vigor)Coined/History Asparagine was isolated in 1806 by French chemist...
- Glucose
Term: glucoseLiterally meaning: ?sweet like?Origin: Greek??????/glycos(=sweet, delightful,) as glycose, an older term for glucose .Coined/History(?)Glucose was discovered in 1747 by German chemist Andreas Marrgraf (1709-1782), who isolated it in raisins....
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
