Biology

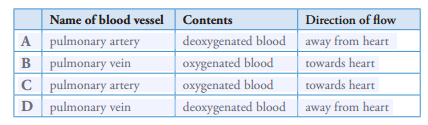
1 A large, thick-walled blood vessel lies alongside a bronchus.
Which row names the vessel and describes its contents?

3 The table shows the presence or absence of ciliated epithelium and goblet cells in airways.
Which row describes a bronchiole?

4 Two airways each have smooth muscle in their walls, but only one has cartilage.
What are the airways?
A alveolus and bronchus
B alveolus and trachea
C bronchiole and bronchus
D bronchus and trachea
5 The mucus secreted into the airways is a solution of the glycoprotein mucin.
Which statement about mucin contains a mistake?
A Carbohydrate chains make mucus sticky enough to trap dust particles.
B Mucus is secreted by goblet cells by the process of endocytosis.
C Carbohydrate chains are added to protein in the Golgi apparatus of goblet cells.
D Mucus is moved over the surface of the airways by the action of ciliated cells.
6 A carbon dioxide molecule dissociates from haemoglobin and diffuses along the shortest path into an alveolus.
Assuming that the molecule diffuses through a gap in a capillary wall, how many phospholipid bilayers did the molecule pass through?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
7 What maintains the diffusion gradient for the diffusion of oxygen out of an alveolus?
1 binding of oxygen with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
2 blood flow bringing a new supply of red blood cells
3 increased surface area of red blood cells as they are forced through narrow capillaries
4 complete replacement of the air in the alveolus with each breath
A 1, 2 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 3 and 4 only
8 What are the adaptations of an alveolus for its role in gas exchange?
1 very thin epithelial walls
2 close contact of walls and capillaries
3 walls with elastic fibres which recoil after stretching, to help force air out
4 stiff walls to prevent collapse of the alveolus when breathing out
A 1, 2 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 1 and 2 only
D 3 and 4 only
9 Which event occurring at an alveolus does not require a red blood cell?
A carbon dioxide dissociates from carbaminohaemoglobin
B carbon dioxide is formed from hydrogencarbonate ions
C carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into an air space
D oxygen binds with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
10 Measurements of an adult?s breathing show that at rest:
Which is not a correct conclusion from these measurements?
A About one sixth of the air in the lungs is replaced by breathing out and then in.
B Almost one third of each breath does not reach a gas exchange surface.
C Large changes in the composition of the air in the alveoli do not occur.
D The volume of air in the alveoli after breathing in is 3.0dm3
Answers to Multiple choice test
- #82 Question 5
The diagram below shows a small part of a human lung as it appears through a microscope. (a) Name the type of blood vessel in which the red blood cell is present. (1 mark)(b) Describe and explain two ways in which the structure of the alveoli, shown...
- #49.2 Gas Exchange And Smoking Syllabus 2016
9.1 The gas exchange system 9.2 Smoking The gas exchange system is responsible for the uptake of oxygen into the blood and excreting carbon dioxide. An understanding of this system shows how cells, tissues and organs function...
- #49.1 Gas Exchange And Smoking Syllabus 2015
? The gas exchange system ? Smoking and smoking-related diseases Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] describe the structure of the human gas exchange system, including the microscopic structure of the walls of the trachea,...
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
Click here for PDFRespiration is the oxidation of nutrients in the living cells to release energy for biological work. Breathing is the exchange of O2 from the atmosphere with CO2 produced by the cells. Respiratory organs· General...
- Respiratory System.
Respiratory System.The cells of our body consume oxygen in order to obtain energy. In this process, called oxidation, the cells burn glucose using oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide, and obtaining the necessary energy to carry out several metabolic processes....
Biology
#51 Summary of Gas exchange

1 Multicellular organisms often have surfaces that are specialised to allow exchange of gases to take place between their bodies and the environment. Alveoli in the lungs form the gas exchange surface in mammals.
2 In the human lungs, air passes down the trachea and through a branching system of airways to reach the alveoli. The airways are lined by a ciliated epithelium with mucus-secreting goblet cells. The epithelium protects the alveoli by moving a carpet of mucus
towards the throat, where it can be swallowed.
3 There are C-shaped rings of cartilage in the trachea and irregularly shaped blocks of cartilage in the bronchus to keep the large airways open and so reduce resistance to the fl ow of air. Smooth muscle in the airways contracts and relaxes to adjust the diameter of the airway.
4 The alveoli are lined by a squamous epithelium that gives a short diff usion distance for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. The alveoli are well supplied with blood by the many capillaries surrounding the gas exchange surface.
5 The constant flow of blood and the continuous ventilation of the lungs maintain concentration gradients between blood and air for oxygen and carbon dioxide.
6 Recoil of the elastic fi bres surrounding the alveoli helps to move air out during expiration.
1. Multiple-choice test
1 A large, thick-walled blood vessel lies alongside a bronchus.
Which row names the vessel and describes its contents?

2 The diagram shows part of the wall of a bronchus in cross-section.

3 The table shows the presence or absence of ciliated epithelium and goblet cells in airways.
Which row describes a bronchiole?

4 Two airways each have smooth muscle in their walls, but only one has cartilage.
What are the airways?
A alveolus and bronchus
B alveolus and trachea
C bronchiole and bronchus
D bronchus and trachea
5 The mucus secreted into the airways is a solution of the glycoprotein mucin.
Which statement about mucin contains a mistake?
A Carbohydrate chains make mucus sticky enough to trap dust particles.
B Mucus is secreted by goblet cells by the process of endocytosis.
C Carbohydrate chains are added to protein in the Golgi apparatus of goblet cells.
D Mucus is moved over the surface of the airways by the action of ciliated cells.
6 A carbon dioxide molecule dissociates from haemoglobin and diffuses along the shortest path into an alveolus.
Assuming that the molecule diffuses through a gap in a capillary wall, how many phospholipid bilayers did the molecule pass through?
A 2
B 3
C 4
D 5
7 What maintains the diffusion gradient for the diffusion of oxygen out of an alveolus?
1 binding of oxygen with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
2 blood flow bringing a new supply of red blood cells
3 increased surface area of red blood cells as they are forced through narrow capillaries
4 complete replacement of the air in the alveolus with each breath
A 1, 2 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 2 and 3 only
D 3 and 4 only
8 What are the adaptations of an alveolus for its role in gas exchange?
1 very thin epithelial walls
2 close contact of walls and capillaries
3 walls with elastic fibres which recoil after stretching, to help force air out
4 stiff walls to prevent collapse of the alveolus when breathing out
A 1, 2 and 3 only
B 1, 2 and 4 only
C 1 and 2 only
D 3 and 4 only
9 Which event occurring at an alveolus does not require a red blood cell?
A carbon dioxide dissociates from carbaminohaemoglobin
B carbon dioxide is formed from hydrogencarbonate ions
C carbon dioxide diffuses from the blood into an air space
D oxygen binds with haemoglobin to form oxyhaemoglobin
10 Measurements of an adult?s breathing show that at rest:
- the volume of air in a single breath is 500cm3
- 350 cm3 of each breath reaches the alveoli
- 2500 cm3 of air remain in the lungs after breathing out.
Which is not a correct conclusion from these measurements?
A About one sixth of the air in the lungs is replaced by breathing out and then in.
B Almost one third of each breath does not reach a gas exchange surface.
C Large changes in the composition of the air in the alveoli do not occur.
D The volume of air in the alveoli after breathing in is 3.0dm3
Answers to Multiple choice test
1. A
2. B
3. C
4. C
5. B
6. B
7. A
8. A
9. C
10. D
2. End-of-chapter questions
2 Cartilage is found in which structure?
3 Which of the following is not a role of elastic fibres in the gas exchange system?
4 Which of the following best describes the process of gas exchange in the lungs?
A Air moves in and out of the alveoli during breathing.
B CO2 diffuses from deoxygenated blood in capillaries into the alveolar air.
C O2 and CO2 diffuse down their concentrations gradients between blood and alveolar air.
D O2 diffuses from alveolar air into deoxygenated blood.
5 The figure shows an alveolus.
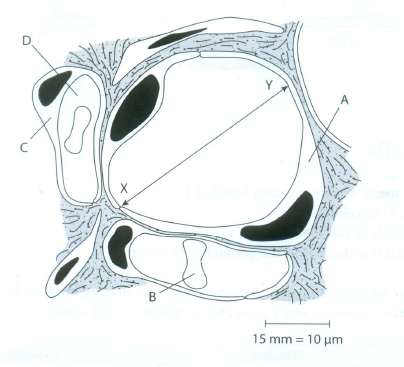 a Name:
a Name:
b Calculate the actual distance indicated by X- Y. Show your working.
c Explain how alveoli are adapted for the exchange of gases.
Total [10]
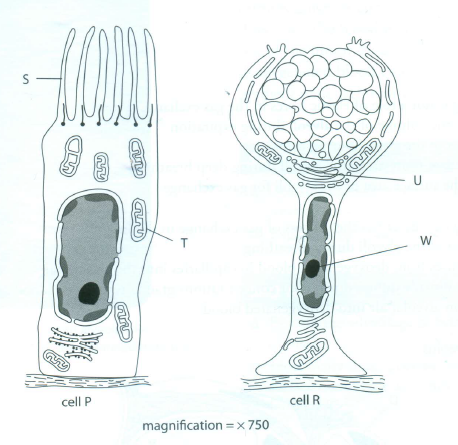
6 The figure shows two cells from the lining of the trachea.
 [5] b Describe how the alveoli are protected against infection.
[5] b Describe how the alveoli are protected against infection.
[Total: 10]
1 A
2 D
3 A
4 C

5 a i A squamous epithelial cell;
B red blood cell;
C endothelial cell; [3]
ii) D plasma; [1]
b distance of scale bar is 15mm 15mm = 10?m X?Y distance measured on page is 47mm 47 ÷ 15 × 10 = 31?m [2]
c (very) large number forming a large surface area;
squamous epithelial cells are very thin to give short diff usion distance;
surrounded by capillaries so well supplied with blood;
capillaries are very close so short diff usion distance;
well ventilated so air constantly refreshed;
maintains concentration gradients for oxygen and carbon dioxide; [max. 4]
[Total: 10]
6 a i P ciliated epithelial cell;
R goblet cell; [2]
ii S cilium/cilia;
T mitochondrion;
U Golgi apparatus;
W nucleolus; [4]
b i T/mitochondria provide energy/ATP;
for movement of cilia; [2]
ii U/Golgi apparatus packages proteins into vesicles;
for secretion; [2]
c length of cell P on page is 80mm 80 ÷ 750 × 0.107mm or 107?m [2]
d cell P: cilia beat/move back and forth;
move mucus;
upwards/towards throat;
cell R: secretes mucus;
mucus traps dust/bacteria/viruses/pollen;
prevents entry to alveoli/gas exchange surface; [max. 4]
[Total: 16]

b mucus secreted;
by mucous glands (in the trachea)/goblet cells (in trachea and bronchi);
bacteria/viruses/pathogens, stick to mucus;
cilia move mucus, upwards/towards throat;
mucus and pathogens swallowed;
destroyed by acid in stomach;
macrophages/phagocytes, in the alveoli;
engulf and digest any pathogens; [max. 5]
[Total: 10]
8 a oxygen diff uses down its concentration gradient;
from alveolar air into red blood cell;
carbon dioxide diff uses down its concentration gradient;
from red blood cells/plasma to alveolar air;
across epithelial cells of alveolus and endothelium of capillary; [max. 4]
b breathing/ventilation;
introduces fresh air/atmospheric air;
removes stale air/air rich in carbon dioxide; [3]
c increase in:
? depth of breathing;
? rate of breathing;
? expansion of alveoli to give a larger surface area;
? diameter of airways; [max. 3]
[Total: 10]
2. End-of-chapter questions
1 The following structures are found in the walls of the gas exchange system.
1 capillaries
2 cilia
3 elastic fibres
4 goblet cells
5 smooth muscle cells
Which would be found in the lining of an alveolus?
A 1 and 3
B 1,2 and 3
C 2 and 5
D 4 and 5
2 Cartilage is found in which structure?
A alveolus
B bronchiole
C capillary
D trachea
3 Which of the following is not a role of elastic fibres in the gas exchange system?
A contract to decrease the volume of the alveoli during expiration
B recoil to force air out of the alveoli during expiration
C stretch to accommodate more air in the alveoli during deep breathing
Dstretch to increase the surface area of the alveoli for gas exchange
4 Which of the following best describes the process of gas exchange in the lungs?
A Air moves in and out of the alveoli during breathing.
B CO2 diffuses from deoxygenated blood in capillaries into the alveolar air.
C O2 and CO2 diffuse down their concentrations gradients between blood and alveolar air.
D O2 diffuses from alveolar air into deoxygenated blood.
5 The figure shows an alveolus.

i cells A, B and C [3]
ii the fluid at D.
b Calculate the actual distance indicated by X- Y. Show your working.
c Explain how alveoli are adapted for the exchange of gases.
Total [10]
6 The figure shows two cells from the lining of the trachea.

a Name:
i cells P and R
ii structures S, T, U and W
b Explain:
i why cell P contains many of the structures labelled T
ii the role of structure U in cell R.
c Calculate the actual length of cell P. Show your working.
d Describe the roles of cell P and cell R in the gas exchange system.
[Total: 16]
7 a Copy and complete the table to compare the trachea with a respiratory bronchiole. Use a tick (v) to indicate that the structure is present and a cross (x) to indicate that it is not.
 [5]
[5][Total: 10]
8 The composition of alveolar air remains fairly constant even though gases are exchanged with the blood in the capillaries that surround the alveoli.
a Describe the process of gas exchange between alveolar air and blood. [4]
b Explain why the composition of alveolar air remains fairly constant.
c Suggest 3 ways in which the gas exchange system responds to the demands of exercise. [3]
[Total: 10]
3. End-of-chapter answers
2 D
3 A
4 C

5 a i A squamous epithelial cell;
B red blood cell;
C endothelial cell; [3]
ii) D plasma; [1]
b distance of scale bar is 15mm 15mm = 10?m X?Y distance measured on page is 47mm 47 ÷ 15 × 10 = 31?m [2]
c (very) large number forming a large surface area;
squamous epithelial cells are very thin to give short diff usion distance;
surrounded by capillaries so well supplied with blood;
capillaries are very close so short diff usion distance;
well ventilated so air constantly refreshed;
maintains concentration gradients for oxygen and carbon dioxide; [max. 4]
[Total: 10]
6 a i P ciliated epithelial cell;
R goblet cell; [2]
ii S cilium/cilia;
T mitochondrion;
U Golgi apparatus;
W nucleolus; [4]
b i T/mitochondria provide energy/ATP;
for movement of cilia; [2]
ii U/Golgi apparatus packages proteins into vesicles;
for secretion; [2]
c length of cell P on page is 80mm 80 ÷ 750 × 0.107mm or 107?m [2]
d cell P: cilia beat/move back and forth;
move mucus;
upwards/towards throat;
cell R: secretes mucus;
mucus traps dust/bacteria/viruses/pollen;
prevents entry to alveoli/gas exchange surface; [max. 4]
[Total: 16]

b mucus secreted;
by mucous glands (in the trachea)/goblet cells (in trachea and bronchi);
bacteria/viruses/pathogens, stick to mucus;
cilia move mucus, upwards/towards throat;
mucus and pathogens swallowed;
destroyed by acid in stomach;
macrophages/phagocytes, in the alveoli;
engulf and digest any pathogens; [max. 5]
[Total: 10]
8 a oxygen diff uses down its concentration gradient;
from alveolar air into red blood cell;
carbon dioxide diff uses down its concentration gradient;
from red blood cells/plasma to alveolar air;
across epithelial cells of alveolus and endothelium of capillary; [max. 4]
b breathing/ventilation;
introduces fresh air/atmospheric air;
removes stale air/air rich in carbon dioxide; [3]
c increase in:
? depth of breathing;
? rate of breathing;
? expansion of alveoli to give a larger surface area;
? diameter of airways; [max. 3]
[Total: 10]
- #82 Question 5
The diagram below shows a small part of a human lung as it appears through a microscope. (a) Name the type of blood vessel in which the red blood cell is present. (1 mark)(b) Describe and explain two ways in which the structure of the alveoli, shown...
- #49.2 Gas Exchange And Smoking Syllabus 2016
9.1 The gas exchange system 9.2 Smoking The gas exchange system is responsible for the uptake of oxygen into the blood and excreting carbon dioxide. An understanding of this system shows how cells, tissues and organs function...
- #49.1 Gas Exchange And Smoking Syllabus 2015
? The gas exchange system ? Smoking and smoking-related diseases Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] describe the structure of the human gas exchange system, including the microscopic structure of the walls of the trachea,...
- Breathing And Exchange Of Gases
Click here for PDFRespiration is the oxidation of nutrients in the living cells to release energy for biological work. Breathing is the exchange of O2 from the atmosphere with CO2 produced by the cells. Respiratory organs· General...
- Respiratory System.
Respiratory System.The cells of our body consume oxygen in order to obtain energy. In this process, called oxidation, the cells burn glucose using oxygen, releasing carbon dioxide, and obtaining the necessary energy to carry out several metabolic processes....
