Biology
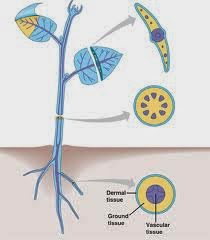 An organ usually contains many different types of cells. These are arranged in a particular pattern characteristic of the organ, with cells of a similar type found together, forming distinctive tissues.
An organ usually contains many different types of cells. These are arranged in a particular pattern characteristic of the organ, with cells of a similar type found together, forming distinctive tissues.
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
There are only 2 basic types of cells, primitive prokaryotes and the more complex eukaryotes.
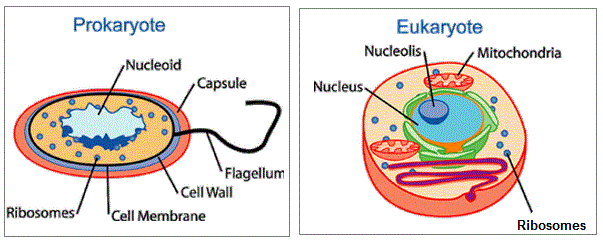
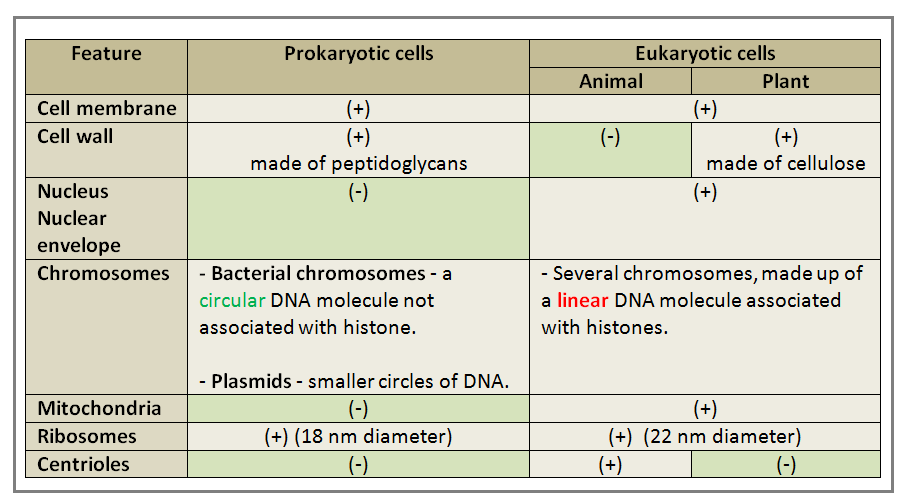
- Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes
While eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells have some characteristics in common, they diverged from their common ancestor billions of years ago, thus accounting for significant differences in overall structure and function. Here we will go over them....
- Q: Compare And Contrast The Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Genomes
The eukaryotic genome is diploid but the prokaryotic genome is haploid. The eukaryotic genome has multiple origins of replication but the prokaryotic genome has only one origin of replication. The eukaryotic genome may have more than one chromosome but...
- #2.2. Cell Structure - Syllabus 2016
1.1 The microscope in cell studies1.2 Cells as the basic units of living organisms All organisms are composed of cells. Knowledge of their structure and function underpins much of biology. The fundamental differences between eukaryotic...
- Eukaryote Vs Prokaryote
Biology EssayMichael McDonald11/17/14Period 7 Cells are categorized into two groups, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. The two cells are similar in some ways , but also they are different in others. One way they are similar is that they both have DNA which...
- Prokaryotic Cells Vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryote is a cell or an organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane enclosed organelles and most of their DNA is a single circular molecule. All bacteria are prokaryotic cells. The word "prokaryote" means "before the nucleus"...
Biology
#5. Plan diagrams of tissue and organ, prokaryotic and eukariotic cells

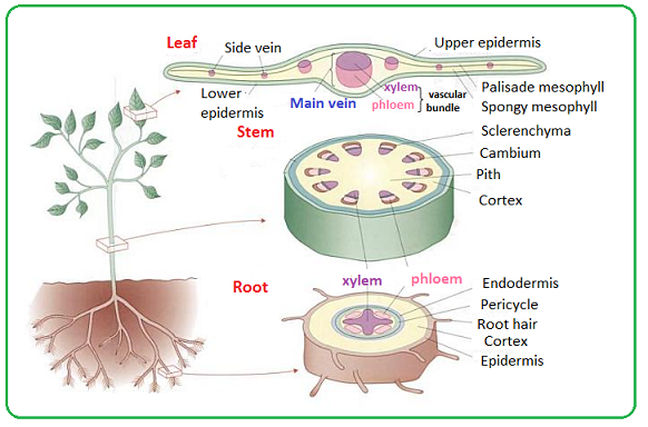 |
| A cross section of leaf, stem and root. |
Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
There are only 2 basic types of cells, primitive prokaryotes and the more complex eukaryotes.
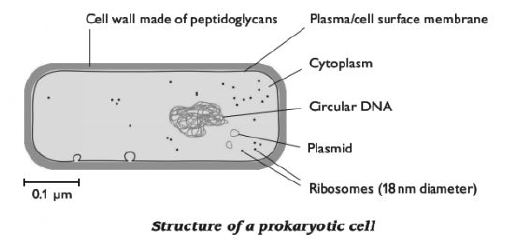
- Prokaryotic cells (Pro=?before?, karyon = ?nucleus?) are evolutionarily ancient. They were here first and for billions of years were the only form of life. Today most life is prokaryotic, and these cells are supremely successful. All bacteria and bacteria-like Archaea are prokaryotic organisms.
- Eukaryotes (Eu=?true?, karyon= ?nucleus?) can be single celled or multi-cellular organisms. Eukaryotic cells are more complex, having evolved from a prokaryote-like predecessor. Most of the living things that we are typically familiar with are composed of eukaryotic cells: animals, plants, fungi and protists.
- much smaller
- no membrane-bound nucleusor other membrane-bound organelles. The only membrane is the plasma membrane.
- the genetic material is naked within the cytoplasm
- ribosomes are the only type of organelle

Eukaryotic cells
The main structure:
- a double membrane-bound nucleus separates the genetic material from the rest of the cell.
- an endomembrane system composed of different membrane-bound organelles that transport materials around the cell: the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus and vesicles.
- energy producing organelles: mitochondria and chloroplasts, involved in metabolism and energy conversion.
Comparison of prokaryotic, animal and plant cells


Syllabus 2015 Characteristics of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (f) [PA] draw and label low power plan diagrams of tissues and organs (including a transverse section of stems, roots and leaves); (i) outline key structural features of typical prokaryotic cells (including: unicellular, 1-5?m diameter, peptidoglycan cell walls, lack of membrane-bound organelles, naked circular DNA, 70S ribosomes) and compare and contrast the structure of prokaryotic cells with eukaryotic cells (reference to mesosomes should not be included); |
Syllabus 2016 d) outline key structural features of typical prokaryotic cells as seen in a typical bacterium (including: unicellular, 1-5µm diameter, peptidoglycan cell walls, lack of organelles surrounded by double membranes, naked circular DNA, 70S ribosomes) e) compare and contrast the structure of typical prokaryotic cells with typical eukaryotic cells (reference to mesosomes should not be included) f) outline the key features of viruses as non-cellular structures (limited to protein coat and DNA/RNA) |
- Prokaryotes Vs Eukaryotes
While eukaryotic cells and prokaryotic cells have some characteristics in common, they diverged from their common ancestor billions of years ago, thus accounting for significant differences in overall structure and function. Here we will go over them....
- Q: Compare And Contrast The Prokaryotic And Eukaryotic Genomes
The eukaryotic genome is diploid but the prokaryotic genome is haploid. The eukaryotic genome has multiple origins of replication but the prokaryotic genome has only one origin of replication. The eukaryotic genome may have more than one chromosome but...
- #2.2. Cell Structure - Syllabus 2016
1.1 The microscope in cell studies1.2 Cells as the basic units of living organisms All organisms are composed of cells. Knowledge of their structure and function underpins much of biology. The fundamental differences between eukaryotic...
- Eukaryote Vs Prokaryote
Biology EssayMichael McDonald11/17/14Period 7 Cells are categorized into two groups, Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic. The two cells are similar in some ways , but also they are different in others. One way they are similar is that they both have DNA which...
- Prokaryotic Cells Vs. Eukaryotic Cells
Prokaryotic Cells Prokaryote is a cell or an organism that lacks a nucleus and other membrane enclosed organelles and most of their DNA is a single circular molecule. All bacteria are prokaryotic cells. The word "prokaryote" means "before the nucleus"...
