Biology
 Proteins are large molecules made of long chains of amino acids.
Proteins are large molecules made of long chains of amino acids.
1. Amino acids
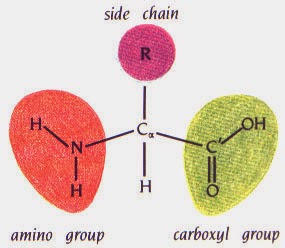
All proteins have the same basic structure. They consist of an Amino Group (NH2), an Carboxyl group (COOH), and a Carbon in the middle which bonds with a Hydrogen atom and an 'R' group, which is specific to individual amino acids.
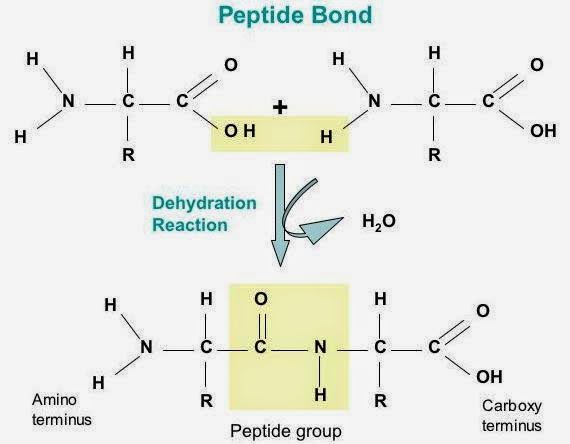
a. Condensation reaction:
- Amino Acid Activation
Codons of an mRNA molecule contain genetic messages that are carried by the mRNA and they need to be translated to form the corresponding sequence of amino acids that will form the polypeptide chain and subsequently the protein. The tRNA transfers amino...
- Translation
What is Translation? Once transcription occurs translation has to then do its job in the ribosomes by taking the base code of a mRNA molecule and translating a peptide into a chain of amino acids. This is how it works: Molecules of mRNA come out of the...
- #13. Protein - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary And Quaternary Structure
Amino acids can be linked together in any order to form a long chain - polypeptide. Protein molecules can be made up of the same polypeptides or different polypeptides. 1. Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- Polypeptide
Term: polypeptideLiterally meaning: ?several peptides?Origin: Greek????-/poly-(=many, several)????????/peptidio(=peptid) a low weight polymer composed of two (dipeptide) or more amino acids joined by peptide bonds consisting...
Biology
#12. Proteins - amino acids, peptid bonds
 Proteins are large molecules made of long chains of amino acids.
Proteins are large molecules made of long chains of amino acids.1. Amino acids
All proteins have the same basic structure. They consist of an Amino Group (NH2), an Carboxyl group (COOH), and a Carbon in the middle which bonds with a Hydrogen atom and an 'R' group, which is specific to individual amino acids.

There are 20 naturally occurring 'R' groups, making amino acids neutral, acidic, alkaline, aromatic (has a ring structure) or sulphur-containing). The 20 R groups corresponds to 20 different amino acids. Each different amino acid has a specific name. For example, Alanine's 'R' group consists of CH3.
2. Peptid bonds
2 amino acids are joined by a peptide bond ---> dipeptide + H2O.

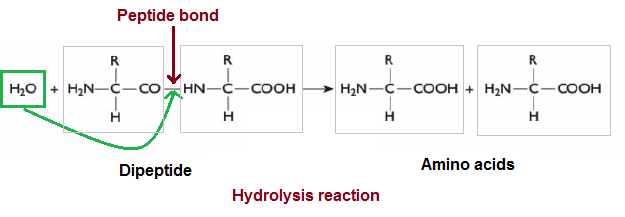
b. Hydrolysis reaction:
Dipeptides are split into 2 amino acids by breaking the peptide bond using a molecule of H20. 
| Syllabus 2015 (f) describe the structure of an amino acid and the formation and breakage of a peptide bond; |
Syllabus 2016 An understanding of protein structure and how it is related to function is central to many aspects of biology, such as enzymes, antibodies and muscle contraction. Globular and fibrous proteins play important roles in biological processes such as the transport of gases and providing support for tissues. a) describe the structure of an amino acid and the formation and breakage of a peptide bond |
- Amino Acid Activation
Codons of an mRNA molecule contain genetic messages that are carried by the mRNA and they need to be translated to form the corresponding sequence of amino acids that will form the polypeptide chain and subsequently the protein. The tRNA transfers amino...
- Translation
What is Translation? Once transcription occurs translation has to then do its job in the ribosomes by taking the base code of a mRNA molecule and translating a peptide into a chain of amino acids. This is how it works: Molecules of mRNA come out of the...
- #13. Protein - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary And Quaternary Structure
Amino acids can be linked together in any order to form a long chain - polypeptide. Protein molecules can be made up of the same polypeptides or different polypeptides. 1. Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- Polypeptide
Term: polypeptideLiterally meaning: ?several peptides?Origin: Greek????-/poly-(=many, several)????????/peptidio(=peptid) a low weight polymer composed of two (dipeptide) or more amino acids joined by peptide bonds consisting...
