Biology
- #80 Question 3
(a) The diagrams show a cell in various stages ofthe mitotic cell cycle. Name the stage represented by each diagram, and arrange them in the correct sequence. (b) Describe the role of spindle microtubules in mitosis. (3 marks) (c) The graph below shows...
- #32 Summary Of Cell And Nuclear Division
1. Growth of a multicellular organism is a result of parent cells dividing to produce genetically identical daughter cells. 2. During cell division the nucleus divides first, followed by division of the whole cell. 3. Division of a nucleus to produce...
- # 30 Mitosis
Mitosis is a nuclear division giving rise to genetically identical cells in which the chromosome number is maintained by the exact duplication of chromosome. Significance of mitosis production of geneticlly identical cells: It keeps the chromosome...
- Anaphase
Term: anaphase Literally meaning: ?toward appearance?Origin: Anc Greek???-/ana-(=prefix denoting up to, toward, against) >???/ana(=up, on, upon before, first)?????/phasis(=stage) > ?????/phasko(=imperfect tense of verb ??????/phemi(=appear, show,...
- Prophase
Eduard Adolf Strasburger(1844-1912)Term: prophase Literally meaning: ?before the appearance?Origin: Anc Greek???/pro(=prefix denoting before, first)?????/phasis(=stage) > ?????/phasko(=imperfect tense of verb ??????/phemi=appear, show,...
Biology
The Cell Cycle
What are all of the stages to the Cell Cycle?
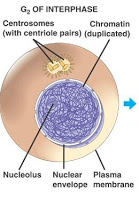
The Cell Cycle starts with its first stage called Interphase. The cell will be in this stage the longest amount of time out of all of the stages of the cycle.
During the first part of Interphase is called the G1 phase. Before the cell goes into the G1 phase it starts out in a resting state and begins to get ready for division. The cell then begins the G1 phase and begins to grow and synthesize amino acids turning them into proteins and then into enzymes.
The next stage of Interphase is called the S phase. This stage begins by DNA synthesis and by the end of the stage there are two sister chromatids.
The last stage of Interphase is called the G2 phase. Once again biosynthesis is happening in the cell making sure that everything is done and that the cell can then move onto Mitosis. Once Interphase is at its end the cell has doubled everything and has two times the amount of material that it needs and can now start Mitosis.

Mitosis is the next stage of the cell cycle. During Mitosis there are multiple stages in itself.
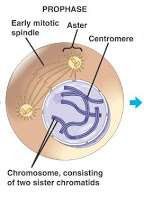
-The first stage of Mitosis is called Prophase. During Prophase the chromatine in the cell condenses and the nuclear envelope dissolves and the spindle is made to move chromosomes.

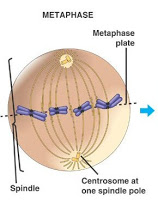
-The second stage is called Metaphase. This is the stage of Mitosis where the chromosomes align going straight across the center of the cell.

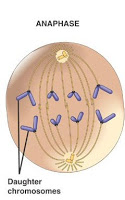
-The third stage is Anaphase. This is where the sister chromatids separate into individual chromatids and move to opposite sides of the cell.

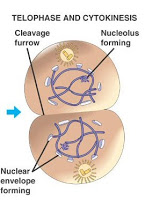
-The final stage of Mitosis is called Telophase. During Telophase a nuclear envelope forms around each of the two sets of chromosomes.

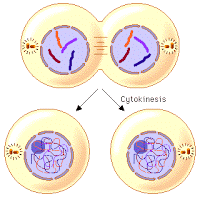
Finally the last part of the Cell Cycle is able to take place. This stage is called Cytokinesis. This is where the cytoplasm of the single cell splits and is then two cells that have the same genetic code.

- #80 Question 3
(a) The diagrams show a cell in various stages ofthe mitotic cell cycle. Name the stage represented by each diagram, and arrange them in the correct sequence. (b) Describe the role of spindle microtubules in mitosis. (3 marks) (c) The graph below shows...
- #32 Summary Of Cell And Nuclear Division
1. Growth of a multicellular organism is a result of parent cells dividing to produce genetically identical daughter cells. 2. During cell division the nucleus divides first, followed by division of the whole cell. 3. Division of a nucleus to produce...
- # 30 Mitosis
Mitosis is a nuclear division giving rise to genetically identical cells in which the chromosome number is maintained by the exact duplication of chromosome. Significance of mitosis production of geneticlly identical cells: It keeps the chromosome...
- Anaphase
Term: anaphase Literally meaning: ?toward appearance?Origin: Anc Greek???-/ana-(=prefix denoting up to, toward, against) >???/ana(=up, on, upon before, first)?????/phasis(=stage) > ?????/phasko(=imperfect tense of verb ??????/phemi(=appear, show,...
- Prophase
Eduard Adolf Strasburger(1844-1912)Term: prophase Literally meaning: ?before the appearance?Origin: Anc Greek???/pro(=prefix denoting before, first)?????/phasis(=stage) > ?????/phasko(=imperfect tense of verb ??????/phemi=appear, show,...
