Biology
![]() Pigments: Carotenoids, Anthocyanins etc.
Pigments: Carotenoids, Anthocyanins etc.![]() Terpenoides: Monoterpenes, Diterpenes etc.
Terpenoides: Monoterpenes, Diterpenes etc. ![]() Drugs: Vinblastin, curcumin etc.
Drugs: Vinblastin, curcumin etc.
In metabolism, there is a series of linked reactions (multistep chemical reaction) called metabolic pathways.
Metabolic pathways are similar to automobile traffic in a city. Flow of metabolites through the metabolic pathways has a definite rate and direction like automobile traffic. This metabolic flow is called dynamic state of body constituents.
Metabolic pathways are 2 types:
1. Anabolic (biosynthetic) pathways: In this, simpler molecules form complex structures. It consumes energy. E.g. formation of acetic acid from cholesterol, assembly of amino acids to protein, photosynthesis etc.
2. Catabolic pathways: In this, complex molecules become simple structures (degradation). It releases energy. E.g. formation of lactic acid from glucose (glycolysis), respiration etc.
The energy released through catabolism is stored in the form of chemical bonds. When needed, this bond energy is utilized for biosynthetic, osmotic and mechanical works. The most important energy currency in living system is the bond energy in adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Organic Compounds
The Four Organic Compounds 1. Carbohydrates are the compound that provide energy to living cells. They are the main energy source because they activate instant cellular energy. The carbohydrates we use as food comes from photosynthesis of plants....
- Catabolic And Anabolic
What exactly are Catabolic and Anabolic reactions?Catabolic and anabolic reactions are both metabolic processes that go to support an organisms metabolism. Catabolic reactions make energy for the cell to use by breaking down large molecules...
- # 66 The Nitrogen Cycle
Living organisms need nitrogen because nitrogen atoms are an essential part of proteins, nucleic acids and ATP. The air contains about 78% nitrogen gas. However, this is in the form of nitrogen molecules, in which two nitrogen atoms are held together...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- Structure Of Living Beings.
Differentiation between living beings and inert matter is an easy question, at least in appearance. This is, however, because we usually think about living things that can be clearly seen growing, moving or, summing up, changing. But if we take...
Biology
Metabolism
METABOLISM

All the biochemical reactions taking place inside a living system together constitute metabolism. E.g.
- Glycolysis
- Kreb's cycle
- Respiration
- Photosynthesis
- Removal of CO2 from amino acids to form amine.
- Removal of amino group in a nucleotide base.
- Hydrolysis of a glycosidic bond etc.
- Primary metabolites: They are the compounds which have identifiable functions and roles in physiological processes. They are not not essential to maintain life. E.g. amino acids, sugars, nucleic acids, lipids, vitamins etc.
- Secondary metabolites: They are not directly involved in normal growth, development or reproduction. They are not not essential to maintain life. E.g.
Alkaloids: Morphine, Codeine etc.
Essential oils: Lemon grass oil etc.
Toxins: Abrin, Ricin etc.
Lectins: Concanavalin A.
Polymeric substances: rubber, gums, cellulose etc.
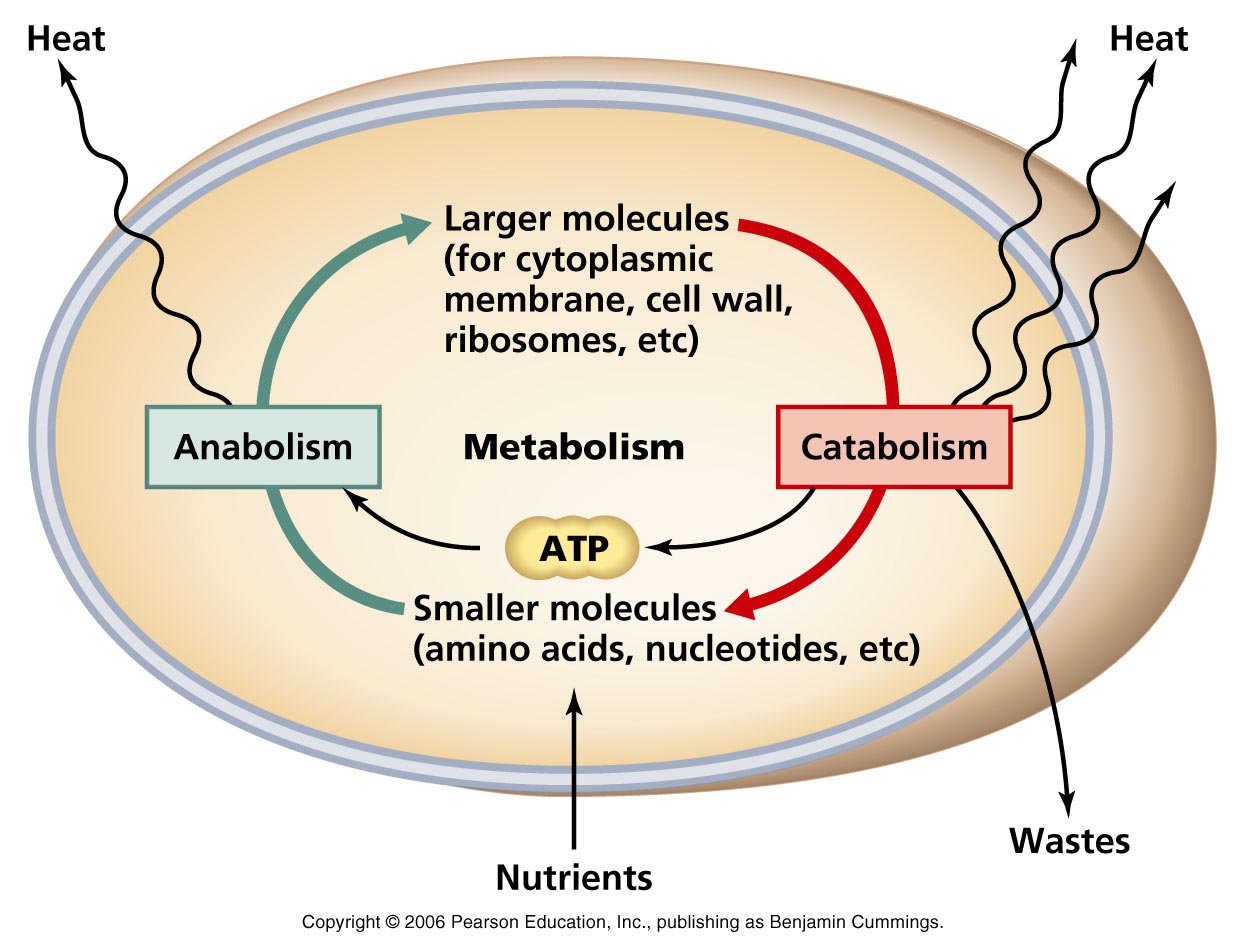
In metabolism, there is a series of linked reactions (multistep chemical reaction) called metabolic pathways.
Metabolic pathways are similar to automobile traffic in a city. Flow of metabolites through the metabolic pathways has a definite rate and direction like automobile traffic. This metabolic flow is called dynamic state of body constituents.
Metabolic pathways are 2 types:
1. Anabolic (biosynthetic) pathways: In this, simpler molecules form complex structures. It consumes energy. E.g. formation of acetic acid from cholesterol, assembly of amino acids to protein, photosynthesis etc.
2. Catabolic pathways: In this, complex molecules become simple structures (degradation). It releases energy. E.g. formation of lactic acid from glucose (glycolysis), respiration etc.
The energy released through catabolism is stored in the form of chemical bonds. When needed, this bond energy is utilized for biosynthetic, osmotic and mechanical works. The most important energy currency in living system is the bond energy in adenosine triphosphate (ATP).
- Organic Compounds
The Four Organic Compounds 1. Carbohydrates are the compound that provide energy to living cells. They are the main energy source because they activate instant cellular energy. The carbohydrates we use as food comes from photosynthesis of plants....
- Catabolic And Anabolic
What exactly are Catabolic and Anabolic reactions?Catabolic and anabolic reactions are both metabolic processes that go to support an organisms metabolism. Catabolic reactions make energy for the cell to use by breaking down large molecules...
- # 66 The Nitrogen Cycle
Living organisms need nitrogen because nitrogen atoms are an essential part of proteins, nucleic acids and ATP. The air contains about 78% nitrogen gas. However, this is in the form of nitrogen molecules, in which two nitrogen atoms are held together...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- Structure Of Living Beings.
Differentiation between living beings and inert matter is an easy question, at least in appearance. This is, however, because we usually think about living things that can be clearly seen growing, moving or, summing up, changing. But if we take...
