Biology
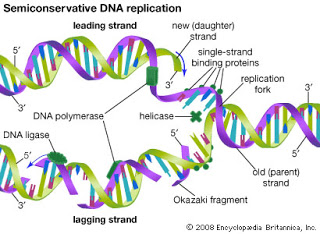

- Q: Explain Why The Two Strands Of Dna Elongate In Opposite Directions
The two strands of DNA are anti parallel. Their 5' to 3' direction is in opposite direction. As the active site of the enzyme DNA polymerase III only recognizes the 3' end of a DNA nucleotide, free nucleotides can only be added in the 3'...
- Q: Compare And Contrast Dna Replication And Transcription
Similarities: Both processes occur in the nucleus. Both processes also involve specific complementary base pairing. Both processes involving the unwinding of the double helix DNA. Both processes involve forming of hydrogen bonds between the original DNA...
- Transcription In Eukaryotic Cells
Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells What is transcription? Transcription is the process that creates RNA inside a cell. It is used to develop proteins inside the cytoplasm of a cell although the actual transcription happens in the nucleus and mitochondria....
- Dna Strands Separate At The Replication Fork
KEY TERMS:A replication fork (Growing point) is the point at which strands of parental duplex DNA are separated so that replication can proceed. A complex of proteins including DNA polymerase is found at the fork. A DNA polymerase is an enzyme that...
- Dna Replication Is Semiconservative
KEY TERMS:A parental strand or duplex of DNA refers to the DNA that will be replicated. The antisense strand (Template strand) of DNA is complementary to the sense strand, and is the one that acts as the template for synthesis of mRNA. A daughter...
Biology
DNA Replication
DNA Replication?
DNA can copy its self over and over again in order to keep creating for the organism it is working for. This action is called DNA replication and takes place in the cell nucleus.

How does DNA replication work? The molecules of DNA are made up of two strands of DNA that are connected together by hydrogen bonds. Hydrogen bonds always form between pairs that complement each other such as adenine compliments thymine and cytosine always pairs with guanine. When a molecule of DNA is trying to split fee of each other, an enzyme, called DNA gyrases, relaxes the strands so that they can split into two separate strands. Then the nucleotides in the nucleus bond with the unpaired bases with the help of DNA polymerase to the split strands and form two new DNA molecules. Once the strands are paired you have two new sets of DNA. Because there is one strand for the original and one new strand the replication process is considered semi-conservative, where one half is conserved from the original pair.

Why are there so many things to do for DNA replication? There are many things that have to happen in order for DNA to be replicated. This is because it carries genetic information and codes for everything in order for the cells to do their jobs. If the code is not replicated correctly then the information passed can cause extreme harm to the cell and the organism to the point where they could both die.

- Q: Explain Why The Two Strands Of Dna Elongate In Opposite Directions
The two strands of DNA are anti parallel. Their 5' to 3' direction is in opposite direction. As the active site of the enzyme DNA polymerase III only recognizes the 3' end of a DNA nucleotide, free nucleotides can only be added in the 3'...
- Q: Compare And Contrast Dna Replication And Transcription
Similarities: Both processes occur in the nucleus. Both processes also involve specific complementary base pairing. Both processes involving the unwinding of the double helix DNA. Both processes involve forming of hydrogen bonds between the original DNA...
- Transcription In Eukaryotic Cells
Transcription in Eukaryotic Cells What is transcription? Transcription is the process that creates RNA inside a cell. It is used to develop proteins inside the cytoplasm of a cell although the actual transcription happens in the nucleus and mitochondria....
- Dna Strands Separate At The Replication Fork
KEY TERMS:A replication fork (Growing point) is the point at which strands of parental duplex DNA are separated so that replication can proceed. A complex of proteins including DNA polymerase is found at the fork. A DNA polymerase is an enzyme that...
- Dna Replication Is Semiconservative
KEY TERMS:A parental strand or duplex of DNA refers to the DNA that will be replicated. The antisense strand (Template strand) of DNA is complementary to the sense strand, and is the one that acts as the template for synthesis of mRNA. A daughter...
