Biology
 It is protected in cranial cavity. It has 3-layered connective tissue membranes (outer dura mater, middle arachnoid mater and inner pia mater) called cranial meninges. The subarachnoid space (space between pia mater and arachnoid mater is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricles of brain are also filled with CSF.
It is protected in cranial cavity. It has 3-layered connective tissue membranes (outer dura mater, middle arachnoid mater and inner pia mater) called cranial meninges. The subarachnoid space (space between pia mater and arachnoid mater is filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricles of brain are also filled with CSF.
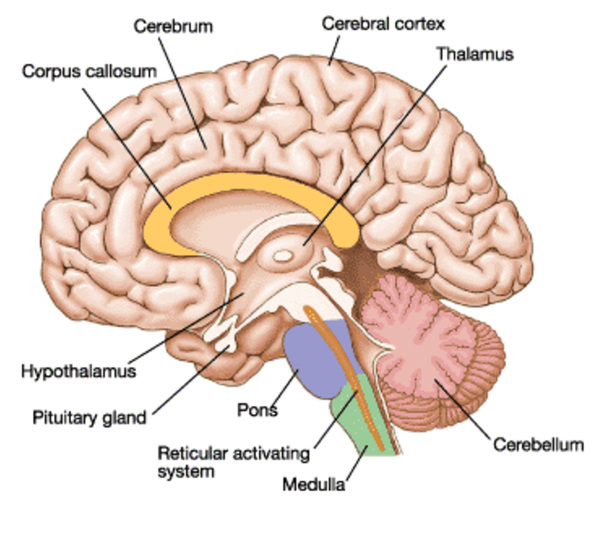
Brain has 3 divisions: Forebrain, Midbrain and Hindbrain.

It is the anterior part. It consists of cerebrum & diencephalon.
The cerebral cortex consists of the following functional areas:
Wernicke?s area: Seen in temporal lobe. Related with understanding speech and language.
Integrated activities of different centres of cerebral cortex control intelligence, memory, judgment, learning, thinking and articulate speech.
Thalamus: It acts as relay station for sensory and motor impulses between cerebrum and other parts of the brain.
Hypothalamus:
Cerebellum (?little cerebrum?):
- Fetal Pig Anatomy Glossary ( I Suggest You Use Ctrl F)
Structure System Primary tissues Functions Pituitary Endocrine Glial cells, bundles of axons, cidophils, basophils and chromophobes cells Secretes hormones, assists other endocrine gland Medulla ...
- Brain/ Development Chart
Name Location Function/characteristics Thalamus Diencephalon process and relay sensory information to parts of the cerebral cortex Optic chiasma Diencephalon The crossing nerves of the eyes Pituitary...
- Thalamus
Term: thalamus Literally meaning: ?inner room? Origin: Anc Greek???????/thalamos(=chamber, inner room ) Coined/Historyby Greek phycisian Galen of Pergamon (130?200 AD in De Usu Partium (Utility of the Parts of the Bode) by way of comparing the human...
- Meninx ( Plural Meninges)
Term: meninx ( plural meninges) Origin: Anc Greek ??????/mininx (=meninx). According Meletios, 7th-8th cen (???????? "???? ??? ??? ???????? ??????????, Migne, ???. 64, ???. 1149) «??? ?? ??????/menin ?? ?????? ??? ?????????" Coined:...
- Neural Control And Co-ordination
NERVOUS (NEURAL) SYSTEM- Controls and coordinates the body activities. - Conducts and integrates the information.- Responses to stimuli. NeuronNeuron is the structural and functional...
Biology
Central Neural System (CNS) - Brain and Spinal cord
CENTRAL NEURAL SYSTEM (CNS)
Central neural system consists of 2 parts: Brain and Spinal cord
A. BRAIN
Brain has 3 divisions: Forebrain, Midbrain and Hindbrain.
a. Forebrain (Prosencephalon)
Cerebrum
It is the largest part. It has 2 cerebral hemispheres held together by a thick tissue (Corpus callosum). Each cerebral hemisphere has 4 lobes. They are Frontal lobe, Parietal lobe, Temporal lobe & Occipital lobe. The cerebral cortex (outer region of cerebrum) has many convulsions (gyri) & depressions (sulci). The gyri increase surface area of the cortex to accommodate more neurons. Cerebral cortex is formed of gray matter and cerebral medulla (inner region) is formed of white matter.The cerebral cortex consists of the following functional areas:
- Motor area: Controls the voluntary movements of muscles. It is found in the posterior parts of frontal lobe.
- Sensory (Somaesthetic) area: Found in parietal lobe (temperature, touch, pressure, pain, taste etc.), occipital lobe (vision) and temporal lobes (hearing & smell).
- Association area: Seen in frontal lobe. It is neither clearly sensory nor motor in function. Responsible for intersensory associations, memory and communication.
Wernicke?s area: Seen in temporal lobe. Related with understanding speech and language.
Integrated activities of different centres of cerebral cortex control intelligence, memory, judgment, learning, thinking and articulate speech.
Diencephalon
It includes thalamus and Hypothalamus. Ventrally in front of the diencephalon, the optic nerves crossover and fuse to form the optic chiasma.Thalamus: It acts as relay station for sensory and motor impulses between cerebrum and other parts of the brain.
Hypothalamus:
- Regulates temperature, thirst, hunger and emotions.
- Secretes 2 hormones called ADH and oxytocin.
- Controls pituitary gland.
- Controls sleep, wakefulness, food intake, blood pressure, heart rate etc.

b. Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
It is located between thalamus/hypothalamus and Pons. A canal (cerebral aqueduct) passes through the mid brain. Mid brain consists of 4 round lobes called Corpora quadrigemina. Their anterior pair is the centre of visual reflexes and the posterior pair is a centre of auditory reflex.c. Hindbrain (Rhombencephalon)
It consists of Cerebellum, Pons varoli & Medulla oblongata. Midbrain and Hind brain together constitute Brain stem.Cerebellum (?little cerebrum?):
Its functions are
- Co-ordination of muscular activities.
- Maintenance of posture and equilibrium.
Its functions are
- It is a bridge between two cerebellar hemispheres.
- Co-ordination of the activities of eye and ear.
- Helps in equilibration and regulation of respiration.
Its functions are
Functions:
- Regulation of respiration, heartbeat, blood pressure, circulation, peristaltic movements etc.
- Centre of salivation, vomiting, sneezing & coughing.
B. SPINAL CORD
It is enclosed within the spinal canal of vertebral column. It is also protected by meninges. Spinal cord has a central canal containing CSF. Unlike brain, spinal cord has outer white matter and inner gray matter.Functions:
- Conduction of impulses to and from the brain.
- Centre of spinal reflexes.
- Fetal Pig Anatomy Glossary ( I Suggest You Use Ctrl F)
Structure System Primary tissues Functions Pituitary Endocrine Glial cells, bundles of axons, cidophils, basophils and chromophobes cells Secretes hormones, assists other endocrine gland Medulla ...
- Brain/ Development Chart
Name Location Function/characteristics Thalamus Diencephalon process and relay sensory information to parts of the cerebral cortex Optic chiasma Diencephalon The crossing nerves of the eyes Pituitary...
- Thalamus
Term: thalamus Literally meaning: ?inner room? Origin: Anc Greek???????/thalamos(=chamber, inner room ) Coined/Historyby Greek phycisian Galen of Pergamon (130?200 AD in De Usu Partium (Utility of the Parts of the Bode) by way of comparing the human...
- Meninx ( Plural Meninges)
Term: meninx ( plural meninges) Origin: Anc Greek ??????/mininx (=meninx). According Meletios, 7th-8th cen (???????? "???? ??? ??? ???????? ??????????, Migne, ???. 64, ???. 1149) «??? ?? ??????/menin ?? ?????? ??? ?????????" Coined:...
- Neural Control And Co-ordination
NERVOUS (NEURAL) SYSTEM- Controls and coordinates the body activities. - Conducts and integrates the information.- Responses to stimuli. NeuronNeuron is the structural and functional...
