Biology
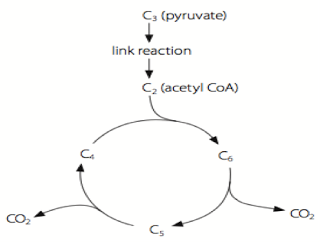 If oxygen is available, each pyruvate now moves into a mitochondrion, where the link reaction and the Krebs cycle take place. During these processes, the glucose is completely oxidised.
If oxygen is available, each pyruvate now moves into a mitochondrion, where the link reaction and the Krebs cycle take place. During these processes, the glucose is completely oxidised.
The link reaction
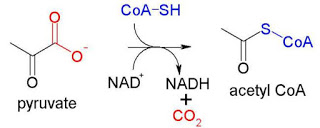
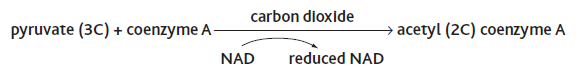
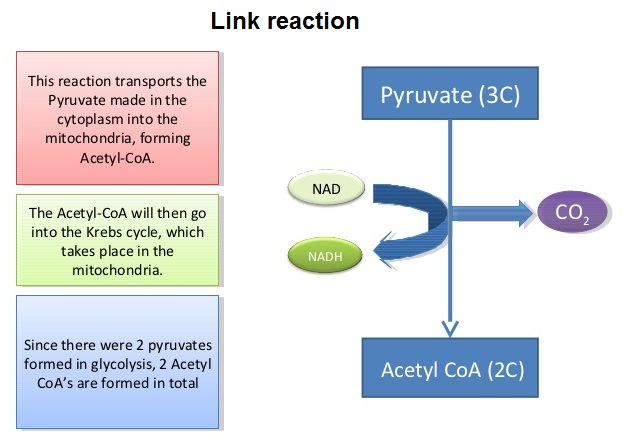
In the link reaction, pyruvate enters the matrix of a mitochondrion and is:
? decarboxylated: CO2 is removed from the pyruvate and then diffuses out of the mitochondrion and out of the cell.
? dehydrogenated: Hydrogen is removed from the pyruvate, and is picked up by NAD, producing reduced NAD. This converts pyruvate into a 2-carbon compound.
? combined with coenzyme A to give acetylcoenzyme A (ACoA).
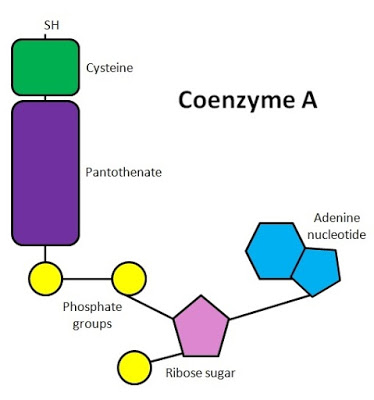
Coenzyme A consists of:
? adenine
? ribose (making a nucleoside together with adenine)
? pantothenic acid (a B vitamin).
Coenzyme A transfers an acetyl group (with 2 carbon atoms) from pyruvate into the Krebs cycle and plays a central role in respiration. It is present in small quantities in a cell and is recycled.
- Krebs Cycle Broken Down
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would not be possible. This is because the Krebs cycle uses the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis to produce...
- Respiration
Respiration is the breakdown of large glucose molecules into simple molecules such as carbon dioxide and water with the simultaneous release of energy inside living cells. It is an enzyme mediated process. Main processes: Glycolysis (glucose to pyruvate,...
- #97 Summary Of Energy And Respiration
1 Organisms must do work to stay alive. The energy input necessary for this work is either light, for photosynthesis, or the chemical potential energy of organic molecules. Work includes anabolic reactions, active transport and movement. Some organisms,...
- # 91 Anaerobic Respiration - Ethanol And Lactate Pathways
Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration that does not use oxygen. It is used when there is not enough oxygen for aerobic respiration. In the absence of free oxygen: Oxidative phosphorylation cannot take place, as there is nothing to accept...
- #89 The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion and is the aerobic phase and requires oxygen. This is also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The Krebs cycle is a series of steps catalysed by enzymes in the matrix:...
Biology
#88 Aerobic respiration, Link reaction

The link reaction
In the link reaction, pyruvate enters the matrix of a mitochondrion and is:
? decarboxylated: CO2 is removed from the pyruvate and then diffuses out of the mitochondrion and out of the cell.
? dehydrogenated: Hydrogen is removed from the pyruvate, and is picked up by NAD, producing reduced NAD. This converts pyruvate into a 2-carbon compound.
? combined with coenzyme A to give acetylcoenzyme A (ACoA).



Coenzyme A consists of:
? adenine
? ribose (making a nucleoside together with adenine)
? pantothenic acid (a B vitamin).
Coenzyme A transfers an acetyl group (with 2 carbon atoms) from pyruvate into the Krebs cycle and plays a central role in respiration. It is present in small quantities in a cell and is recycled.

Syllabus: 12.1 Energy d) outline the roles of the coenzymes A in respiration 12.2 Respiration c) explain that, when oxygen is available, pyruvate is converted into acetyl (2C) coenzyme A in the link reaction |
- Krebs Cycle Broken Down
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would not be possible. This is because the Krebs cycle uses the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis to produce...
- Respiration
Respiration is the breakdown of large glucose molecules into simple molecules such as carbon dioxide and water with the simultaneous release of energy inside living cells. It is an enzyme mediated process. Main processes: Glycolysis (glucose to pyruvate,...
- #97 Summary Of Energy And Respiration
1 Organisms must do work to stay alive. The energy input necessary for this work is either light, for photosynthesis, or the chemical potential energy of organic molecules. Work includes anabolic reactions, active transport and movement. Some organisms,...
- # 91 Anaerobic Respiration - Ethanol And Lactate Pathways
Anaerobic respiration is a type of respiration that does not use oxygen. It is used when there is not enough oxygen for aerobic respiration. In the absence of free oxygen: Oxidative phosphorylation cannot take place, as there is nothing to accept...
- #89 The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion and is the aerobic phase and requires oxygen. This is also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The Krebs cycle is a series of steps catalysed by enzymes in the matrix:...
