Biology
 Carbohydrates:
Carbohydrates:
- Sugar polymers
- Molecules contain C, H, O atoms
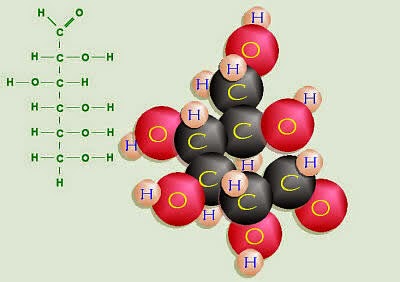
- H atoms are twice as many as C or O atoms (C6H12O6)
Functions of monosaccharides and disaccharides
- Organic Compounds
The Four Organic Compounds 1. Carbohydrates are the compound that provide energy to living cells. They are the main energy source because they activate instant cellular energy. The carbohydrates we use as food comes from photosynthesis of plants....
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #10.tests For Carbohydrates
Tests for Reducing sugars, Non-reducing sugar and Starch. 1. Reducing sugar (Benedict's test) All monosaccharides and most disaccharides (except sucrose) will reduce blue CuSO4(II), producing a precipitate of red Cu2O(I).Benedict?s...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- #7.1 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2015
? Structure of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and their roles in living organisms ? Water and living organisms Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] carry out tests for reducing and non-reducing sugars (including using colour...
Biology
#8. Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, disaccharides

- Sugar polymers
- Molecules contain C, H, O atoms
- H atoms are twice as many as C or O atoms (C6H12O6)
Monosaccharides
- The simplest carbohydrates
- They are sugar: C = 3 = triose C = 4 = tetrose C = 5 = pentose C = 6 = hexose
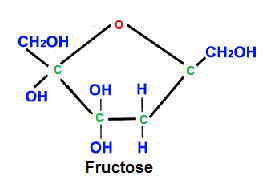
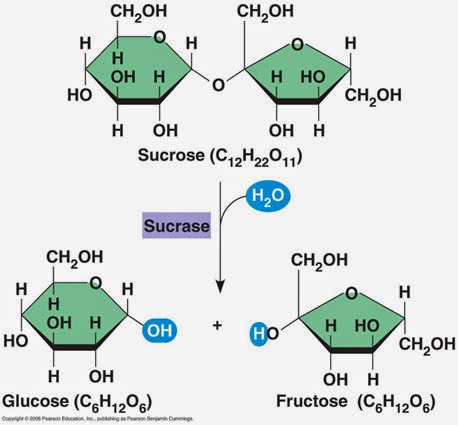
- Examples of hexose sugars: glucose, fructose, galactose (C6H1206)
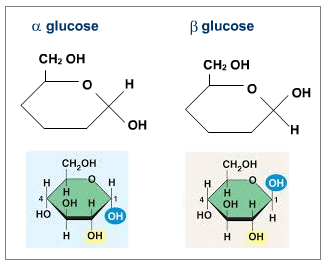
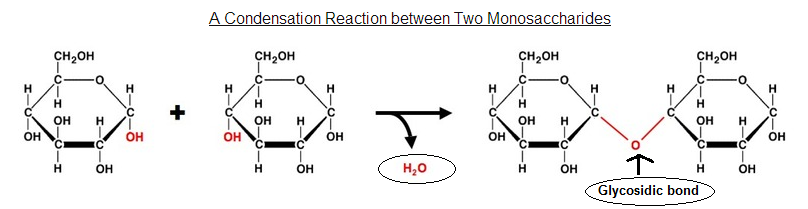
- Molecules often have the form of a ring, made up of some C atoms and one O atom.

- Glucose molecules has 2 forms: ?-glucose and ?-glucose.

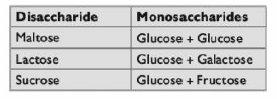
Disaccharides
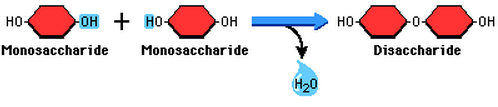
- Different disaccharides can be formed by linking different monosaccharides. The bond that joins them together = glycosidic bond.

- Condensation reactions (dehydration): 2 monosaccharides covalently joined; H20 is formed.


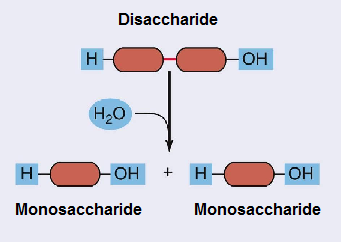
- Hydrolysis reaction (splitting by water): disaccharides are split into 2 monosaccharides by breaking the glycosidic bond; a molecule of H20 is added.


Functions of monosaccharides and disaccharides
- Good sources of energy in living organisms, used in respiration for making ATP.
- Transportable through the body because of the solubility: glucose is transported dissolved in blood plasma (animal), sucrose is transported in phloem sap (plant).
- All monosaccharides and some disaccharides are reducing sugars (reduce blue Benedict's solution to produce an orange-red precipitate). Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar.
| Syllabus 2015 (b) describe the ring forms of ?-glucose and ?-glucose (candidates should be familiar with the terms monomer, polymer and macromolecule); |
Syllabus 2016 Carbohydrates and lipids Carbohydrates and lipids have important roles in the provision and storage of energy and for a variety of other functions such as providing barriers around cells: the phospholipid bilayer of all cell membranes and the cellulose cell walls of plant cells. a) describe the ring forms of ?-glucose and ?-glucose b) define the terms monomer, polymer, macromolecule, monosaccharide, disaccharide and polysaccharide |
- Organic Compounds
The Four Organic Compounds 1. Carbohydrates are the compound that provide energy to living cells. They are the main energy source because they activate instant cellular energy. The carbohydrates we use as food comes from photosynthesis of plants....
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #10.tests For Carbohydrates
Tests for Reducing sugars, Non-reducing sugar and Starch. 1. Reducing sugar (Benedict's test) All monosaccharides and most disaccharides (except sucrose) will reduce blue CuSO4(II), producing a precipitate of red Cu2O(I).Benedict?s...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- #7.1 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2015
? Structure of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and their roles in living organisms ? Water and living organisms Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] carry out tests for reducing and non-reducing sugars (including using colour...
