Biology
 Tests for Reducing sugars, Non-reducing sugar and Starch.
Tests for Reducing sugars, Non-reducing sugar and Starch.
1. Reducing sugar (Benedict's test)

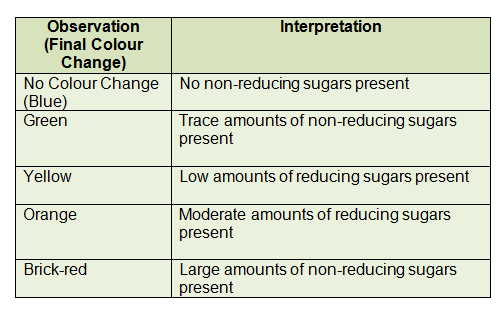
2. Non-reducing sugar (Benedict's test)
- Homework
Plan an experiment to test the hypothesis that acidity affects the germination of a seed. You need to identify all the varaibles: Independent, dependent and controlled. You need to have a control group and explain clearly how you control all the variables...
- #19. Following The Course Of An Enzyme-catalysed Reaction
Measurement of the rate of formation of the product or the rate of disappearance of the substrate. 1. Measurement of the rate of formation of O2 in the reaction: Mash up some biological material like potato tuber or celery stalks, mix them...
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #8. Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, Disaccharides
Carbohydrates: - Sugar polymers - Molecules contain C, H, O atoms - H atoms are twice as many as C or O atoms (C6H12O6) Monosaccharides The simplest carbohydrates They are sugar: C = 3 = triose C = 4 = tetrose C = 5...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
Biology
#10.Tests for carbohydrates

1. Reducing sugar (Benedict's test)
- All monosaccharides and most disaccharides (except sucrose) will reduce blue CuSO4(II), producing a precipitate of red Cu2O(I).
- Benedict?s reagent is an aqueous solution of Cu SO4(II), Na2CO3 and sodium citrate.
- 2 cm³ test solution + ? 2 cm³ Benedict?s reagent.
- Shake, and heat for a few minutes at 95°C in a water bath.
- The mass of precipitate or intensity of the colour indicates the amount of reducing sugar present ---> the test is semi-quantitative.


2. Non-reducing sugar (Benedict's test)
Principles:

Additional resource: mrothery.co.uk
- Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar (not reduce CuSO4) ---> Benedict's test (-) .
- If it is hydrolysed to form glucose and fructose ---> Benedict's test (+) .
- So sucrose is the only sugar that will give a (-) Benedict's test before hydrolysis and a (+) test afterwards.
Steps:
- Test a sample for reducing sugars to be sure it does not contain reducing sugars.
- Boil the test solution with dilute HCl for a few minutes to hydrolyse the glycosidic bond.
- Neutralise the solution by gently adding small amounts of solid NaHCO3 until it stops fizzing.
- Test for reducing sugar.
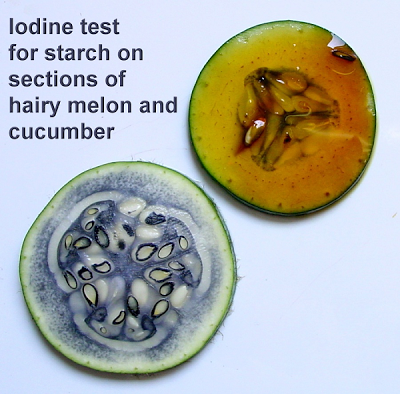
- 2 cm³ of test solution + 2 drops of iodine/KI solution.
- A blue-black colour indicates the presence of starch as a starch-polyiodide complex is formed.
- Starch is only slightly soluble in water, but the test works well in a suspension or as a solid.


Additional resource: mrothery.co.uk
| Syllabus 2015 (a) [PA] carry out tests for reducing and non-reducing sugars (including using colour standards as a semi-quantitative use of the Benedict?s test), the iodine in potassium iodide solution test for starch, the emulsion test for lipids and the biuret test for proteins; |
Syllabus 2016 Testing for biological molecules Tests for biological molecules can be used in a variety of contexts, such as identifying the contents of mixtures of molecules and following the activity of digestive enzymes. a) carry out tests for reducing sugars and non-reducing sugars, the iodine in potassium iodide solution test for starch, the emulsion test for lipids and the biuret test for proteins to identify the contents of solutions b) carry out a semi-quantitative Benedict?s test on a reducing sugar using dilution, standardising the test and using the results (colour standards or time to first colour change) to estimate the concentration |
- Homework
Plan an experiment to test the hypothesis that acidity affects the germination of a seed. You need to identify all the varaibles: Independent, dependent and controlled. You need to have a control group and explain clearly how you control all the variables...
- #19. Following The Course Of An Enzyme-catalysed Reaction
Measurement of the rate of formation of the product or the rate of disappearance of the substrate. 1. Measurement of the rate of formation of O2 in the reaction: Mash up some biological material like potato tuber or celery stalks, mix them...
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #8. Carbohydrates - Monosaccharides, Disaccharides
Carbohydrates: - Sugar polymers - Molecules contain C, H, O atoms - H atoms are twice as many as C or O atoms (C6H12O6) Monosaccharides The simplest carbohydrates They are sugar: C = 3 = triose C = 4 = tetrose C = 5...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
