Biology
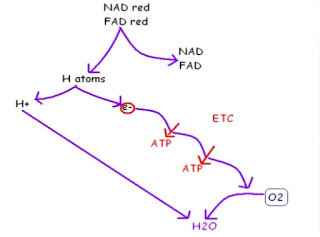
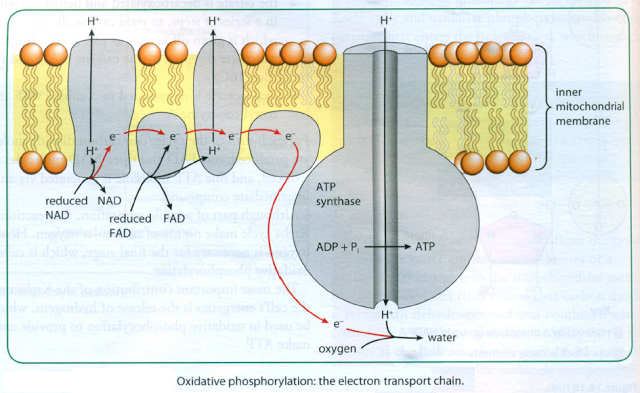
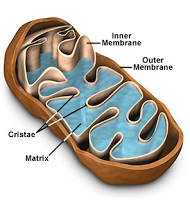 In the final stage of aerobic respiration, oxidative phosphorylation, the energy for the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP comes from the activity of the electron transport chain (ETC). Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane, the cristae.
In the final stage of aerobic respiration, oxidative phosphorylation, the energy for the phosphorylation of ADP to ATP comes from the activity of the electron transport chain (ETC). Oxidative phosphorylation takes place in the inner mitochondrial membrane, the cristae.
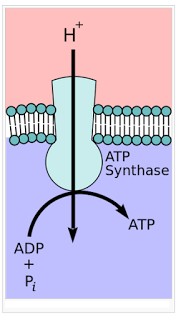
The H+ are allowed to diffuse back into the matrix through special channel proteins that work as ATPases.The movement of the H+ through the ATPases provides enough energy to cause ADP and inorganic phosphate to combine to make ATP.
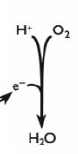
At the end of the chain, the electrons reunite with the protons from which they were originally split. They combine with oxygen to produce water. This is why oxygen is required in aerobic respiration - it acts as the final acceptor for the hydrogens removed from the respiratory substrate during glycolysis, the link reaction and the Krebs cycle.

The sequence of events in the respiration
- Krebs Cycle Broken Down
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would not be possible. This is because the Krebs cycle uses the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis to produce...
- Q: Discuss The Role Of Membranes In The Synthesis Of Atp During Photosynthesis
The chloroplast is enclosed by two membranes, and this separates reactions within the chloroplast from the rest of the cytoplasm. The double membrane of the chloroplast also serves to maintain high substrate concentrations within the chloroplast for photosynthesis....
- #97 Summary Of Energy And Respiration
1 Organisms must do work to stay alive. The energy input necessary for this work is either light, for photosynthesis, or the chemical potential energy of organic molecules. Work includes anabolic reactions, active transport and movement. Some organisms,...
- #94 Structure And Function Of The Mitochondrion
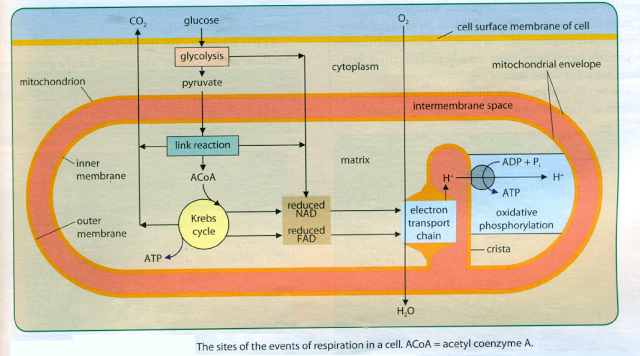
The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell (ATP) and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur....
- #85 Energy And Respiration - Syllabus 2016
12.1 Energy12.2 Respiration Energy is a fundamental concept in biology. All living things require a source of cellular energy to drive their various activities. ATP is the universal energy currency as its molecules are small,...
Biology
# 90 Oxidative phosphorylation and Electron transport chain

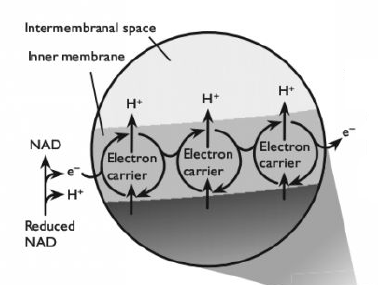
Hydrogens from reduced FAD and reduced NAD first pass to hydrogen carriers in the inner membrane and are then split are split into protons (H+) and electrons (e-).
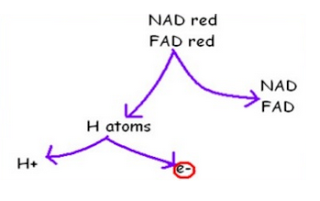
The electrons pass along a series of electron carriers on the ETC of the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. Each of these electron carriers is at a lower energy level than its predecessor. As the electrons move along the chain, they lose energy. This energy is used to actively transport H+ from the matrix of the mitochondrion, across the inner membrane and into the space between the inner and outer membranes. This builds up a high concentration of H+ in this space.

The electrons pass along a series of electron carriers on the ETC of the inner membrane of the mitochondrion. Each of these electron carriers is at a lower energy level than its predecessor. As the electrons move along the chain, they lose energy. This energy is used to actively transport H+ from the matrix of the mitochondrion, across the inner membrane and into the space between the inner and outer membranes. This builds up a high concentration of H+ in this space.



Summary of the oxidative phosphorylation:



The sequence of events in the respiration


Syllabus: 12.1 Energy e) explain that the synthesis of ATP is associated with the electron transport chain on the membranes of mitochondria and chloroplasts 12.2 Respiration f) outline the process of oxidative phosphorylation including the role of oxygen as the final electron acceptor (no details of the carriers are required) g) explain that during oxidative phosphorylation: ? energetic electrons release energy as they pass through the electron transport system ? the released energy is used to transfer protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane ? protons return to the mitochondrial matrix by facilitated diffusion through ATP synthase providing energy for ATP synthesis (details of ATP synthase are not required) |
- Krebs Cycle Broken Down
The Krebs cycle, also known as the Citric Acid cycle, is a very important process in cellular respiration. Without this portion, respiration would not be possible. This is because the Krebs cycle uses the pyruvate molecules from glycolysis to produce...
- Q: Discuss The Role Of Membranes In The Synthesis Of Atp During Photosynthesis
The chloroplast is enclosed by two membranes, and this separates reactions within the chloroplast from the rest of the cytoplasm. The double membrane of the chloroplast also serves to maintain high substrate concentrations within the chloroplast for photosynthesis....
- #97 Summary Of Energy And Respiration
1 Organisms must do work to stay alive. The energy input necessary for this work is either light, for photosynthesis, or the chemical potential energy of organic molecules. Work includes anabolic reactions, active transport and movement. Some organisms,...
- #94 Structure And Function Of The Mitochondrion
The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell (ATP) and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur....
- #85 Energy And Respiration - Syllabus 2016
12.1 Energy12.2 Respiration Energy is a fundamental concept in biology. All living things require a source of cellular energy to drive their various activities. ATP is the universal energy currency as its molecules are small,...
