Biology
- Mitosis
Prophase Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Centrioles migrate to opposite poles of the cells (except in plant cells which do not have centrioles). Microtubules develop and form a star shaped structure known as an aster, and spindle fibres may develop....
- Eukaryotic Cells
Cell Webquest ? Ms. Carter Eukaryotic Cells California Standard: Cell Biology 1.a, e, f, g CELL BIOLOGY 1 a. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism?s...
- #4. Cell Structure And Function
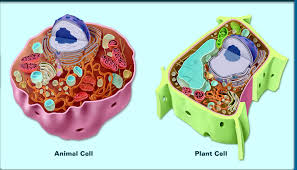
Describe and interpret drawings and photographs of typical animal and plant cells. Note that plant cells are always surrounded by a cell wall made of cellulose, never found around animal cells. Typical animal and plant cells as seen using...
- Comparison Between Cytokinesis In Plant Cell And Animal Cell
Cytokinesis in plant cell and animal cell: Major Differences Cytokinesis in plant cell Cytokinesis in animal cell 1. Mechanism of cytokinesis is cell plate. By cell furrow. 2. Spindle...
- Comparison Between Prokaryotic Cell And Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell 1. Lack of organized nucleus. Genetic material is present in the form of nucleiod Well organized nucleus 2. Nuclear membrane...
Biology
Comparison between plant cell and animal cell
| Plant cell | Animal cell |
| 1. Usually larger in size | Comparatively smaller in size |
| 2. It is enclosed by a rigid cell wall in addition to plasma membrane | No cell wall |
| 3. It cannot change its shape | It can often change in shape |
| 4. Plastids are present. Plant cells exposed to sunlight contain chloroplast | Plastids are usually absent |
| 5. A mature plant cell contains a large central vacuole | An animal cell often possesses many small vacuole |
| 6. Nucleus lies on one side in the peripheral cytoplasm | Nucleus usually lies in the centre |
| 7. Centrioles are usually absent except in motile cells of lower plants | Centrioles are practically present in all animal cells |
| 8. Lysosomes are rare | Lysosomes are always present |
| 9. Glyoxysomes may be present | Absent |
| 10. Tight junctions and desmosomes are lacking | They are present |
| 11. Reserve food is generally in the form of starch | Reserve food is usually glycogen |
| 12. It can synthesize all the amino acids, coenzymes and vitamins required by them | It cannot synthesize all the amino acids, coenzymes and vitamins required by them |
| 13. Spindle formed during cell division is anastral i.e. without asters at esthe poles | Spindle formed during cell division is amphiastral i.e. has an aster at each pole |
| 14. Cytokinesis occurs by cell plate method | Cytokinesis occurs by constriction or furrowing |
| 15. Plant cell does not burst if placed in hypotonic solution due to the presence of the cell wall | Animal cells lacking contractile vacuoles usually burst, if placed in hypotonic solution |
- Mitosis
Prophase Chromatin condenses to form chromosomes. Centrioles migrate to opposite poles of the cells (except in plant cells which do not have centrioles). Microtubules develop and form a star shaped structure known as an aster, and spindle fibres may develop....
- Eukaryotic Cells
Cell Webquest ? Ms. Carter Eukaryotic Cells California Standard: Cell Biology 1.a, e, f, g CELL BIOLOGY 1 a. The fundamental life processes of plants and animals depend on a variety of chemical reactions that occur in specialized areas of the organism?s...
- #4. Cell Structure And Function
Describe and interpret drawings and photographs of typical animal and plant cells. Note that plant cells are always surrounded by a cell wall made of cellulose, never found around animal cells. Typical animal and plant cells as seen using...
- Comparison Between Cytokinesis In Plant Cell And Animal Cell
Cytokinesis in plant cell and animal cell: Major Differences Cytokinesis in plant cell Cytokinesis in animal cell 1. Mechanism of cytokinesis is cell plate. By cell furrow. 2. Spindle...
- Comparison Between Prokaryotic Cell And Eukaryotic Cell
Prokaryotic cell Eukaryotic cell 1. Lack of organized nucleus. Genetic material is present in the form of nucleiod Well organized nucleus 2. Nuclear membrane...
