Biology
- #42 Summary Of Transport In Multicellular Plants
1. Multicellular organisms with small surface area to volume ratios need transport systems. 2. Water and mineral salts are transported through a plant in xylem vessels. Movement of water is a passive process in which the water moves down a water...
- #41 Transport In Phloem
The movement of substances in phloem tissue is called translocation. The main substances that are moved are sucrose and amino acids, which are in solution in water. These substances have been made by the plant and are called assimilates. Phloem...
- #40 Movement Of Water And Minerals In The Xylem
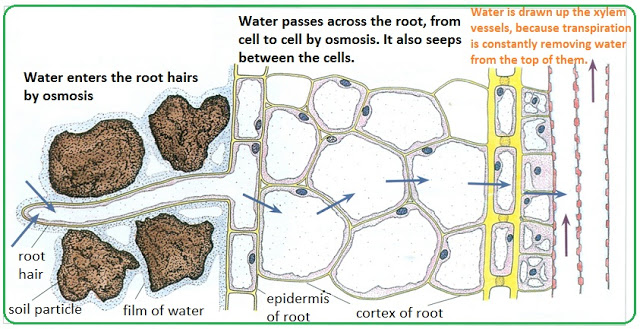
Most plants secure the water and minerals they need from their roots. The path taken is: soil -> roots -> stems -> leaves. The minerals (e.g., K+, Ca2+) travel dissolved in the water. Water and minerals enter the root by separate paths which...
- # 25 Passive And Active Transport Across Cell Membranes
Substances can enter or leave a cell in 2 ways: 1) Passive a) Simple Diffusion b) Facilitated Diffusion c) Osmosis (water only) 2) Active a) Molecules b) Particles I. Passive transport across cell membranes 1. Diffusion Molecules and ions move...
- #38.1 Transport In Multicellular Plants - Syllabus 2015
? The need for, and functioning of, a transport system in multicellular plants Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the need for transport systems in multicellular plants and animals in terms of size and surface area to...
Biology
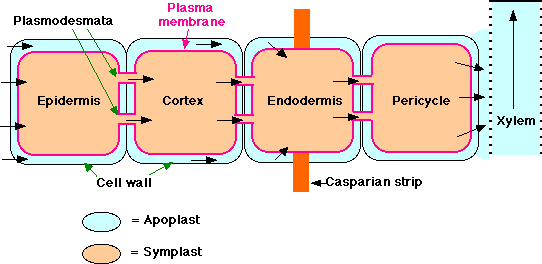
Comparison between Active absorption and Passive absorption of water in plants
Major differences between Active absorption and Passive absorption of water in plants
| Active absorption of water | Passive absorption of water |
| It occurs due to the activity of root and root hairs. | It occurs mainly due to the activity of upper part of the plant such as shoot and leaves. |
| Water is absorbed by the osmotic or non-osmotic processes along or against DPD gradient. | Water is absorbed as a result of tension created by transpiration pull. |
| It involves symplast (via. Protoplasm) movement of water. | It involves apoplast movement of water. i.e., through cell walls and intercellular spaces. |
| It utilizes metabolic energy. | It utilizes solar energy for transpiration. |
| Root cells play an active role. | Root cells play a passive role. |
| It is independent of transpiration. | It takes place when transpiration is fast. |
| It creates a positive pressure in the xylem channels. | It produces a negative pressure in xylem channels. |

- #42 Summary Of Transport In Multicellular Plants
1. Multicellular organisms with small surface area to volume ratios need transport systems. 2. Water and mineral salts are transported through a plant in xylem vessels. Movement of water is a passive process in which the water moves down a water...
- #41 Transport In Phloem
The movement of substances in phloem tissue is called translocation. The main substances that are moved are sucrose and amino acids, which are in solution in water. These substances have been made by the plant and are called assimilates. Phloem...
- #40 Movement Of Water And Minerals In The Xylem
Most plants secure the water and minerals they need from their roots. The path taken is: soil -> roots -> stems -> leaves. The minerals (e.g., K+, Ca2+) travel dissolved in the water. Water and minerals enter the root by separate paths which...
- # 25 Passive And Active Transport Across Cell Membranes
Substances can enter or leave a cell in 2 ways: 1) Passive a) Simple Diffusion b) Facilitated Diffusion c) Osmosis (water only) 2) Active a) Molecules b) Particles I. Passive transport across cell membranes 1. Diffusion Molecules and ions move...
- #38.1 Transport In Multicellular Plants - Syllabus 2015
? The need for, and functioning of, a transport system in multicellular plants Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) explain the need for transport systems in multicellular plants and animals in terms of size and surface area to...
