Biology
 A respiratory substrate is a molecule from which energy can be liberated to produce ATP in a living cell. Glucose is not the only respiratory substrate. All carbohydrates, lipids and proteins can also be used as respiratory substrates.
A respiratory substrate is a molecule from which energy can be liberated to produce ATP in a living cell. Glucose is not the only respiratory substrate. All carbohydrates, lipids and proteins can also be used as respiratory substrates.
Many cells in the human body are able to use a range of different respiratory substrates. However, brain cells can only use glucose. Heart muscle preferentially uses fatty acids.


Respiratory quotients
It is possible to get a good idea of which respiratory substrate the cells in an organism are using by measuring the volume of oxygen it is taking in and the volume of carbon dioxide it is giving out.

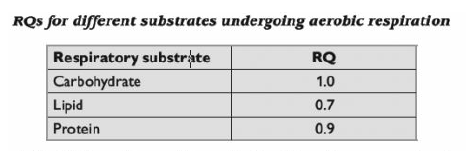
The values in the table are for aerobic respiration. If a cell or an organism is respiring anaerobically, then no oxygen is being used. The RQ is therefore infinity (00).
- #97 Summary Of Energy And Respiration
1 Organisms must do work to stay alive. The energy input necessary for this work is either light, for photosynthesis, or the chemical potential energy of organic molecules. Work includes anabolic reactions, active transport and movement. Some organisms,...
- #94 Structure And Function Of The Mitochondrion
The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell (ATP) and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur....
- #89 The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion and is the aerobic phase and requires oxygen. This is also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The Krebs cycle is a series of steps catalysed by enzymes in the matrix:...
- #85 Energy And Respiration - Syllabus 2016
12.1 Energy12.2 Respiration Energy is a fundamental concept in biology. All living things require a source of cellular energy to drive their various activities. ATP is the universal energy currency as its molecules are small,...
- Q & A
Questions Plants derive energy from the _____________ of Glucose into __________. The time in which a cell oxidizes glucose is known as______. The oxidation of glucose into pyruvate is a process known as__________. What is the energy released during glycolysis...
Biology
#93 Respiratory substrates, Respiratory quotions

Many cells in the human body are able to use a range of different respiratory substrates. However, brain cells can only use glucose. Heart muscle preferentially uses fatty acids.

- Glucose is an essential fuel for some cells, e.g. brain cells, red blood cells and lymphocytes, but some cells, e.g. liver cells, also oxidise lipids and excess amino acids.
- The fatty acid components of lipids are important: carbon atoms are detached in pairs as ACoA and fed into the Krebs cycle.
- Amino acids are deaminated and their carbon?hydrogen skeletons converted into pyruvate or into ACoA.
The energy values of these different substrates are not the same.
Energy values of respiratory substrates
Most of the energy released in respiration comes from the oxidation of hydrogen to water. The more hydrogens there are (in comparison with carbon or oxygen atoms) in the structure of a molecule, the greater the energy value. It is hydrogen atoms that are used to generate ATP via the electron transport chain.
Fatty acids have more hydrogens per unit mass than carbohydrates, so lipids have a greater energy value per unit mass (lipid provides more than twice as much energy per gram as carbohydrate or protein). Energy values in kJ g?1 are determined by burning a known mass of the substance in oxygen in a bomb calorimeter. Typical energy values are:

Respiratory quotients
It is possible to get a good idea of which respiratory substrate the cells in an organism are using by measuring the volume of oxygen it is taking in and the volume of carbon dioxide it is giving out.


- #97 Summary Of Energy And Respiration
1 Organisms must do work to stay alive. The energy input necessary for this work is either light, for photosynthesis, or the chemical potential energy of organic molecules. Work includes anabolic reactions, active transport and movement. Some organisms,...
- #94 Structure And Function Of The Mitochondrion
The mitochondrion is a power plant and industrial park of the cell where energy stored in the bonds of carbohydrates is converted to a form more useful to the cell (ATP) and certain essential biochemical conversions of amino acids and fatty acids occur....
- #89 The Krebs Cycle
The Krebs cycle occurs in the matrix of the mitochondrion and is the aerobic phase and requires oxygen. This is also known as the citric acid cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. The Krebs cycle is a series of steps catalysed by enzymes in the matrix:...
- #85 Energy And Respiration - Syllabus 2016
12.1 Energy12.2 Respiration Energy is a fundamental concept in biology. All living things require a source of cellular energy to drive their various activities. ATP is the universal energy currency as its molecules are small,...
- Q & A
Questions Plants derive energy from the _____________ of Glucose into __________. The time in which a cell oxidizes glucose is known as______. The oxidation of glucose into pyruvate is a process known as__________. What is the energy released during glycolysis...
