Biology
 Lymphocytes, unlike phagocytes, act against specific pathogens. Each lymphocyte contains a set of genes that codes for the production of a particular type of receptor. We have many million different types, each producing just one type of receptor.
Lymphocytes, unlike phagocytes, act against specific pathogens. Each lymphocyte contains a set of genes that codes for the production of a particular type of receptor. We have many million different types, each producing just one type of receptor.
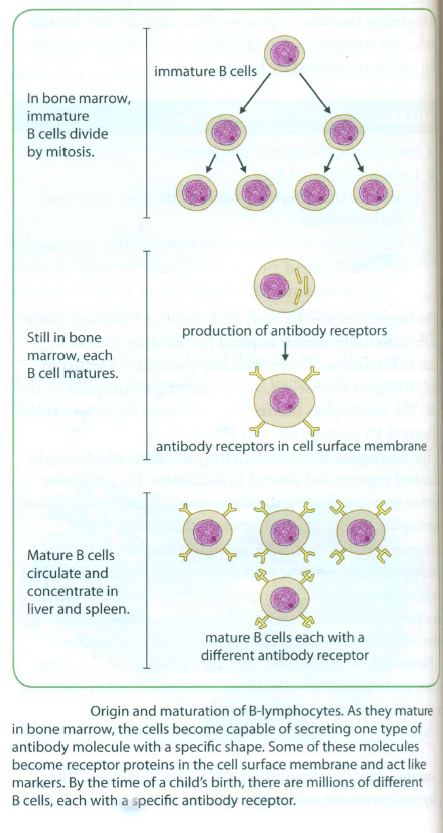
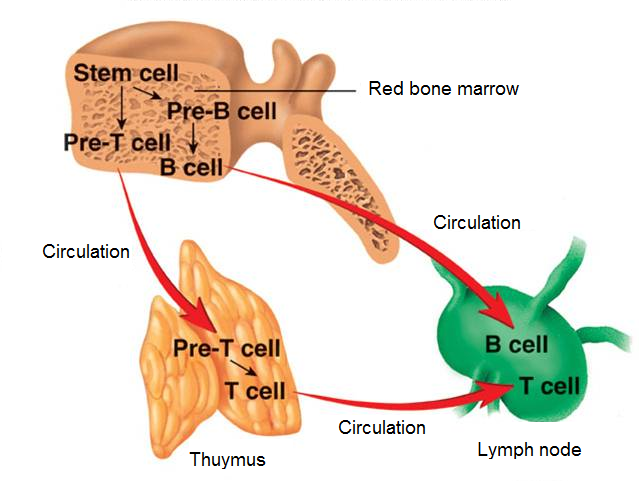
Both B-lymphocytes and T-lymphocytes are made in bone marrow. B-lymphocytes then spread through the body and settle in lymph nodes, although some continue to circulate in the blood. T-lymphocytes collect in the thymus gland, where they mature before spreading into the same areas as B-lymphocytes. The thymus gland disappears at around the time of puberty.
Both types of lymphocyte have a large, rounded nucleus that takes up most of the cell. They can only be told apart by their different actions.
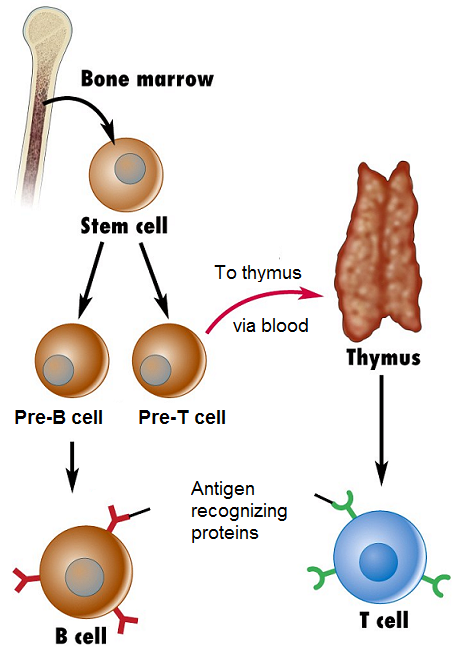
During the maturation process, any lymphocytes that produce receptors that would bind with those on the body's own cells are destroyed. This means that the remaining lymphocytes will only act against non-self molecules that are not normally found in the body. Non-self molecules, such as those on the surfaces of invading bacteria, are called antigens.
- # 61 Action Of T-lymphocytes
T-lymphocytes include T helper cells and T killer cells. Both of these types of cell place their specific receptors in their cell surface membranes. On encountering the relevant antigen, they are activated and divide by mitosis to form...
- # 58 The Immune System - Phagocytes
Credit: Pass My Exams.The human immune system is made up of the organs and tissues involved in destroying pathogens inside the body. There are 2 main groups of cells involved: ? phagocytes: ingest and digest pathogens or infected cells; ? lymphocytes: ...
- #57.2 Immunity - Syllabus 2016
11.1 The immune system 11.2 Antibodies and vaccination An understanding of the immune system shows how cells and molecules function together to protect the body against infectious diseases and how the body is protected from further...
- #57 Immunity - Syllabus 2015
? The immune system ? Vaccination Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope; (b) state the origin and describe the mode of action of phagocytes (macrophages and neutrophils); (c) describe...
- Immunity And Immune System
IMMUNE SYSTEM It is the system that gives immunity to the body by recognizing, responding and remembering foreign antigens. It plays role in allergic reaction, auto-immune disease and organ transplantation. It includes lymphoid organs, tissues, cells...
Biology
#59 The immune response - Lymphocytes




Syllabus 2015 ? The immune system (d) explain the meaning of the term immune response, making reference to the terms antigen, self and non-self; |
Syllabus 2016 11.1 The immune system d) explain the meaning of the term immune response, making reference to the terms antigen, self and non-self |
- # 61 Action Of T-lymphocytes
T-lymphocytes include T helper cells and T killer cells. Both of these types of cell place their specific receptors in their cell surface membranes. On encountering the relevant antigen, they are activated and divide by mitosis to form...
- # 58 The Immune System - Phagocytes
Credit: Pass My Exams.The human immune system is made up of the organs and tissues involved in destroying pathogens inside the body. There are 2 main groups of cells involved: ? phagocytes: ingest and digest pathogens or infected cells; ? lymphocytes: ...
- #57.2 Immunity - Syllabus 2016
11.1 The immune system 11.2 Antibodies and vaccination An understanding of the immune system shows how cells and molecules function together to protect the body against infectious diseases and how the body is protected from further...
- #57 Immunity - Syllabus 2015
? The immune system ? Vaccination Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] recognise phagocytes and lymphocytes under the light microscope; (b) state the origin and describe the mode of action of phagocytes (macrophages and neutrophils); (c) describe...
- Immunity And Immune System
IMMUNE SYSTEM It is the system that gives immunity to the body by recognizing, responding and remembering foreign antigens. It plays role in allergic reaction, auto-immune disease and organ transplantation. It includes lymphoid organs, tissues, cells...
