Biology
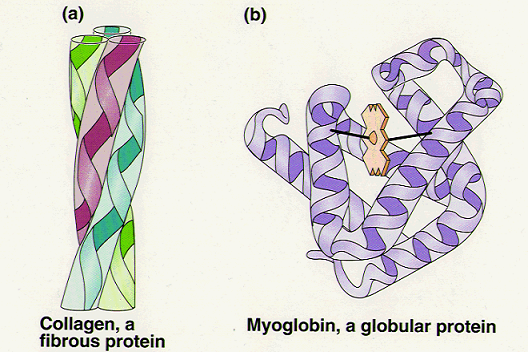 Globular and Fibrous are 2 main types of proteins with a 3D structure.
Globular and Fibrous are 2 main types of proteins with a 3D structure.
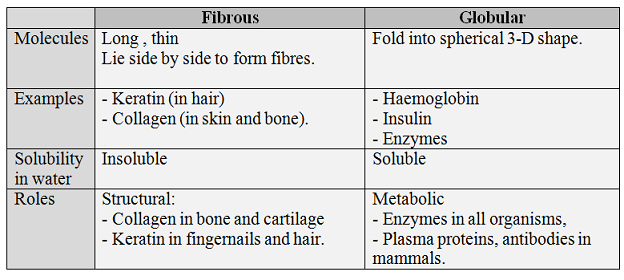
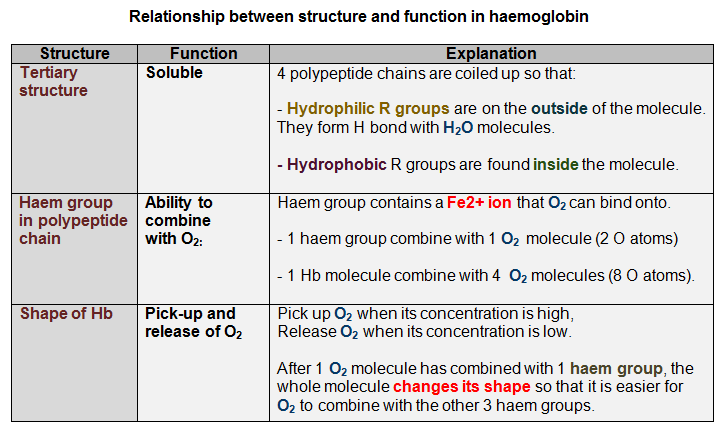
3. Test for proteins
The Biuret Test shows the presence of peptide bonds, which are the basis for the formation of proteins. These bonds will make the blue Biuret reagent turn purple.
Add biuret solution. A purple colour indicates the presence of protein.

- Q: Compare And Contrast The Structure Of Collagen And Cellulose
The monomer of collagen is an amino acid whereas the monomer of cellulose is beta-glucose. The monomers in collagen are linked by peptide bonds whereas those of cellulose are beta (1,4)-glycosidic bonds. Collagen is an alpha helix polypeptide with a turn...
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #13. Protein - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary And Quaternary Structure
Amino acids can be linked together in any order to form a long chain - polypeptide. Protein molecules can be made up of the same polypeptides or different polypeptides. 1. Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
Biology
#14. Globular and fibrous proteins - haemoglobin and collagen


1. Haemoglobin, a globular protein
- Composed of 2 ? + 2 ? polypeptide chains + 1 inorganic prosthetic haem group.
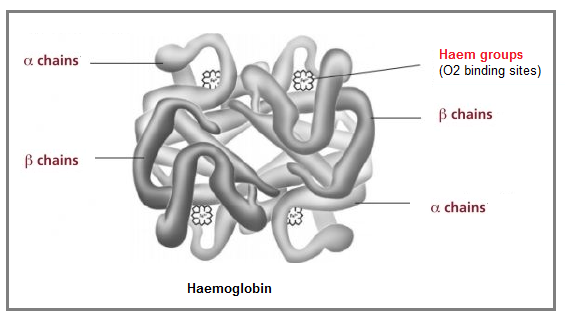 |
| Hb's function: carry O2 from lungs to respiring tissues. |

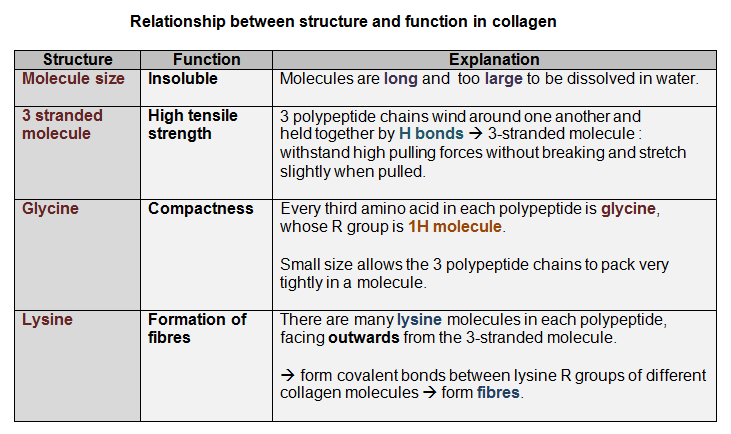
2. Collagen - a fibrous protein
- Collagen molecules wrapped around each other ---> Collagen Fibrils
- Composed of 3 polypeptide chains wound around each other. Each chain is a coil itself of around 1000 amino acids.
- Structure strength is increased by forming:
- Collagen molecules wrapped around each other ---> Collagen Fibrils
- Collagen Fibrils ---> Collagen Fibres.
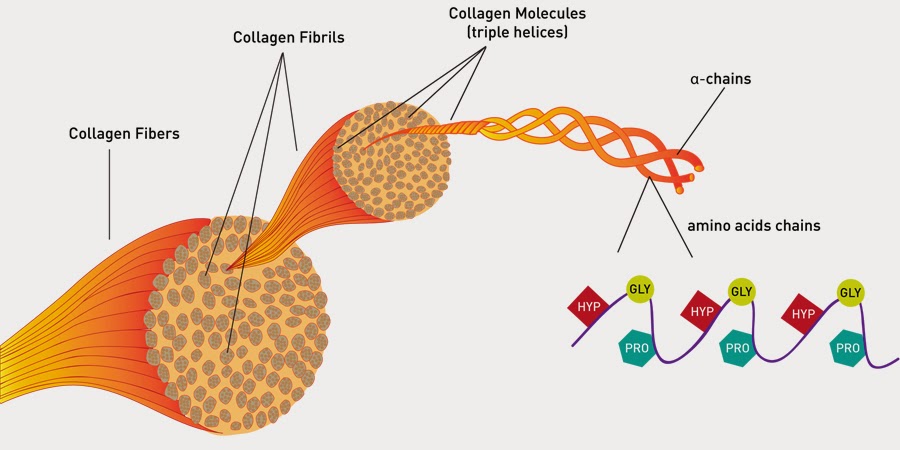 |
Collagen's function: support and elasticity in many animal tissues (human skin, bone and tendons). |

The Biuret Test shows the presence of peptide bonds, which are the basis for the formation of proteins. These bonds will make the blue Biuret reagent turn purple.
Add biuret solution. A purple colour indicates the presence of protein.

| Syllabus 2015 (h) describe the molecular structure of haemoglobin as an example of a globular protein, and of collagen as an example of a fibrous protein and relate these structures to their functions (the importance of iron in the haemoglobin molecule should be emphasised. A haemoglobin molecule is composed of 2 alpha (?) chains and 2 beta (?) chains, although when describing the chains the terms ?-globin and ?-globin may be used. There should be a distinction between collagen molecules and collagen fibres); |
Syllabus 2016 c) describe the molecular structure of haemoglobin as an example of a globular protein, and of collagen as an example of a fibrous protein and relate these structures to their functions (The importance of iron in the haemoglobin molecule should be emphasised. A haemoglobin molecule is composed of two alpha (?) chains and two beta (?) chains, although when describing the chains the terms ?-globin and ?-globin may be used. There should be a distinction between collagen molecules and collagen fibres) |
- Q: Compare And Contrast The Structure Of Collagen And Cellulose
The monomer of collagen is an amino acid whereas the monomer of cellulose is beta-glucose. The monomers in collagen are linked by peptide bonds whereas those of cellulose are beta (1,4)-glycosidic bonds. Collagen is an alpha helix polypeptide with a turn...
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #13. Protein - Primary, Secondary, Tertiary And Quaternary Structure
Amino acids can be linked together in any order to form a long chain - polypeptide. Protein molecules can be made up of the same polypeptides or different polypeptides. 1. Primary structure: The sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide or protein...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- Proteins
PROTEINSProteins are polypeptides. i.e., linear chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A Peptide bond is formed when ?COOH group of one amino acid reacts with ?NH2 group of next amino acid by releasing a molecule of water (dehydration). Proteins...
