Biology
 Lipids:
Lipids:
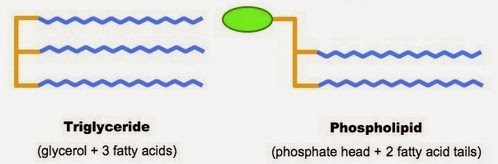
- Include triglycerides + phospholipids.
- Molecules contain C, H, O atoms
- Very small proportion of O.
- Insoluble in water.
1.Triglycerides
- Made of glycerol 'backbone', attached to 3 fatty acids by ester bonds.


3. Emulsion (Ethanol) test for lipids
- Lipid Used For Energy Storage
All lipids share a common characteristic; they do not mix well with water. Fats are lipids that are mainly energy-storing molecules. Fats consist of glycerol linked to three fatty acids. The cooking oil above is an unsaturated fatty acid. Unsaturated...
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- #7.1 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2015
? Structure of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and their roles in living organisms ? Water and living organisms Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] carry out tests for reducing and non-reducing sugars (including using colour...
- Comparison Between Saturated And Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids Unsaturated fatty acids 1. They do not possess any double bond in their carbon chains They possess one or more double bonds in their carbon chains 2. ...
Biology
#11. Lipids - Triglycerides and Phospholipids.

- Include triglycerides + phospholipids.
- Molecules contain C, H, O atoms
- Very small proportion of O.
- Insoluble in water.
1.Triglycerides
- Made of glycerol 'backbone', attached to 3 fatty acids by ester bonds.

Fatty acids

Triglycerides are insoluble in water ---> energy storage in plants, animals and fungi. They contain more energy per gram than polysaccharides.
b.In plants
Triglycerides = major part of energy stores in seeds:
- Have long chains of C and H atoms.
- Each C atom has 4 bonds: 2 to C atoms, 2 to H atoms.
- Sometime, only 1 H atom attached --> C atom has a 'spare' bond, attached to the next-door C atom (also has 1 H bonded) ---> double bond.
- Unsaturated fatty acids has ? 1 C-C double bonds (do not contain quite as much H).
- Saturated fatty acids has no double bonds.

- Lipids containing unsaturated fatty acids ---> unsaturated lipids (in plant)
- Lipids containing completely saturated fatty acids ---> saturated lipids (in animal)
- Unsaturated lipids tend to have lower melting points than saturated lipids.
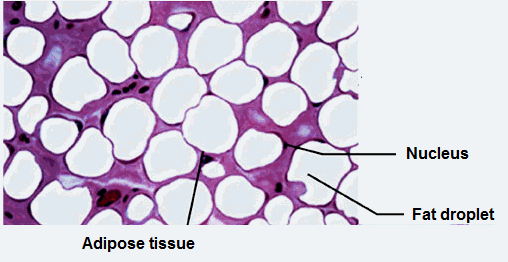
a. In mammals
Triglyceride are build up beneath the skin in the form of adipose tissue:

- It cells contain oil droplets of triglycerides;
- Helps to insulate body against heat loss.
- Relatively low density ---> ? buoyancy ---> useful for aquatic mammals living in cold water (whales, seals).
- Forms a protective layer around organs (e.g. kidneys).
Triglycerides = major part of energy stores in seeds:
- Cotyledons (sunflower seeds...)
- Endosperm (castor beans...).
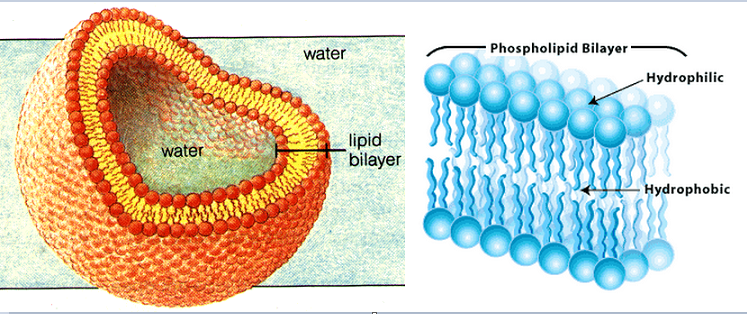
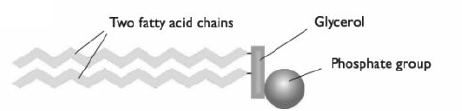
- Made of glycerol 'backbone', 2 fatty acids and 1 phosphate group.


- Fatty acid chains are hydrophobic: no electrical charge ---> not attracted to H2O molecules.
- Phosphate group is hydrophilic: has electrical charge ---> attracted to H2O molecules.
- In H2O, phospholipid molecules arranges into a bilayer: hydrophilic heads facing outwards into the water + hydrophobic tails facing inwards, avoiding water.
- This is the basic structure of a cell membrane.


- Dissolve the substance by mixing it with absolute ethanol.
- Decant the ethanol into water.
- If lipids are present in the mixture, it will precipitates and forms an milky emulsion.
 |
| A milky emulsion indicates the presence of lipid. |
Syllabus 2015 (e) describe the molecular structure of a triglyceride and a phospholipid and relate these structures to their functions in living organisms; |
Syllabus 2016 f) describe the molecular structure of a triglyceride with reference to the formation of ester bonds and relate the structure of triglycerides to their functions in living organisms g) describe the structure of a phospholipid and relate the structure of phospholipids to their functions in living organisms |
- Lipid Used For Energy Storage
All lipids share a common characteristic; they do not mix well with water. Fats are lipids that are mainly energy-storing molecules. Fats consist of glycerol linked to three fatty acids. The cooking oil above is an unsaturated fatty acid. Unsaturated...
- #16 Summary Of Biological Molecules
From small to large 1. The larger biological molecules are made from smaller molecules. Polysaccharides are made from monosaccharides, proteins from amino acids, nucleic acids from nucleotides, lipids from fatty acids and glycerol. 2. Polysaccharides,...
- #7.2 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2016
2.1 Testing for biological molecules 2.2 Carbohydrates and lipids 2.3 Proteins and water This section introduces carbohydrates, proteins and lipids: organic molecules that are important in cells. Nucleic...
- #7.1 Biological Molecules - Syllabus 2015
? Structure of carbohydrates, lipids and proteins and their roles in living organisms ? Water and living organisms Learning Outcomes Candidates should be able to: (a) [PA] carry out tests for reducing and non-reducing sugars (including using colour...
- Comparison Between Saturated And Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Saturated fatty acids Unsaturated fatty acids 1. They do not possess any double bond in their carbon chains They possess one or more double bonds in their carbon chains 2. ...
