Biology
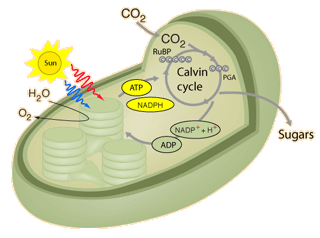 The light-independent reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplast, where the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, usually known as rubisco, is found.
The light-independent reactions take place in the stroma of the chloroplast, where the enzyme ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase, usually known as rubisco, is found.
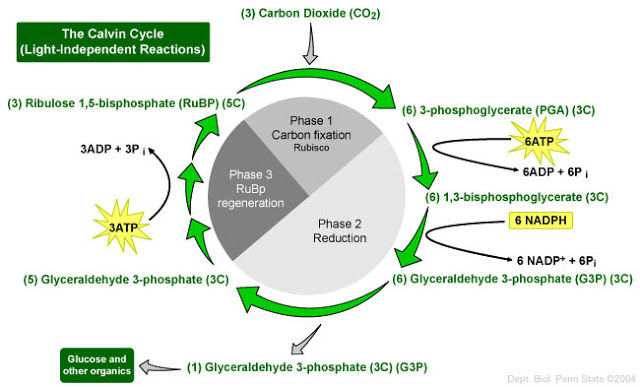
2. Reduction
Energy from ATP and hydrogen from reduced NADP are then used to convert the GP into triose phosphate, TP. Triose phosphate is the first carbohydrate produced in photosynthesis.
3. RuBP regeneration
Most of the triose phosphate is used to produce ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), so that more carbon dioxide can be fixed.
The rest is used to make glucose or whatever other organic substances the plant cell requires. These include:
- #104 Separating Chlorophyll Pigments By Thin Layer Chromatography (tlc)
Chromatography is a method of separation that relies on the different solubilities of different solutes in a solvent. A mixture of chlorophyll pigments is dissolved in a solvent, and then a small spot is placed onto chromatography paper. The solvent gradually...
- # 102 The Light-dependent Reactions, Photophosphorilation
Chlorophyll molecules in photosystern I (PSI) and photosystern II (PSII) absorb light energy. The energy excites electrons, raising their energy level so that they leave the chlorophyll. The chlorophyll is said to be photo-activated. PSII contains...
- #101 Photosynthetic Pigments
Photosynthetic pigments are pigments presented in chloroplasts or photosynthetic bacteria. They capture light energy necessary for photosynthesis and convert it to chemical energy. PigmentsA pigment is any substance that absorbs light.The color...
- #100 Chloroplasts
Photosynthesis takes place inside chloroplasts. These are organelles surrounded by 2 membranes, called an envelope. Chloroplasts are found in mesophyll cells in leaves: - Palisade mesophyll cells contain most chloroplasts. - Spongy...
- #98 Photosynthesis Syllabus
13.1 Photosynthesis as an energy transfer process 13.2 Investigation of limiting factors 13.3 Adaptations for photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the energy transfer process that is the basis of much of life on Earth....
Biology
#103 The light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle)


1. Carbon fixation
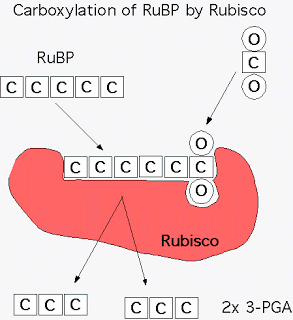
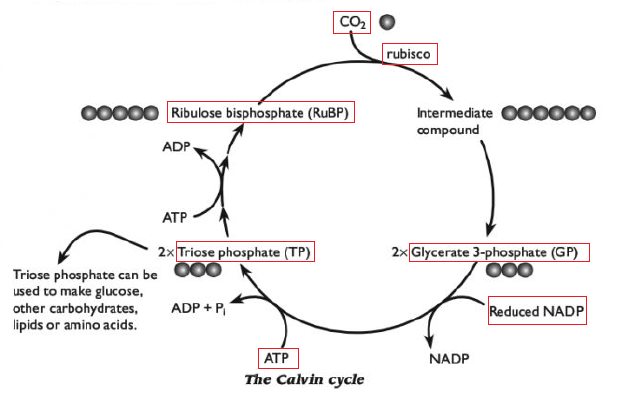
CO2 diffuses into the stroma from the air spaces within the leaf. It enters the active site of rubisco, which combines it with a 5-carbon compound called ribulose bisphosphate, RuBP. The reaction is called carbon fixation.
The products of this reaction are two 3-carbon molecules, glycerate 3-phosphate, GP.
The products of this reaction are two 3-carbon molecules, glycerate 3-phosphate, GP.

2. Reduction
Energy from ATP and hydrogen from reduced NADP are then used to convert the GP into triose phosphate, TP. Triose phosphate is the first carbohydrate produced in photosynthesis.
Most of the triose phosphate is used to produce ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), so that more carbon dioxide can be fixed.
The rest is used to make glucose or whatever other organic substances the plant cell requires. These include:
- polysaccharides such as starch for energy storage and cellulose for making cell walls,
- sucrose for transport,
- amino acids for making proteins,
- lipids for energy storage
- nucleotides for making DNA and RNA.

Syllabus: 13.1 Photosynthesis as an energy transfer process Light energy absorbed by chloroplast pigments in the light dependent stage of photosynthesis is used to drive reactions of the light independent stage that produce complex organic compounds. Chromatography is used to identify chloroplast pigments and was also used to identify the intermediates in the Calvin cycle. a) explain that energy transferred as ATP and reduced NADP from the light dependent stage is used during the light independent stage (Calvin cycle) of photosynthesis to produce complex organic molecules b) state the sites of the light dependent and the light independent stages in the chloroplast c) describe the role of chloroplast pigments (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b, carotene and xanthophyll) in light absorption in the grana d) interpret absorption and action spectra of chloroplast pigments e) use chromatography to separate and identify chloroplast pigments and carry out an investigation to compare the chloroplast pigments in different plants (reference should be made to Rf values in identification) f) describe the light dependent stage as the photoactivation of chlorophyll resulting in the photolysis of water and the transfer of energy to ATP and reduced NADP (cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation should be described in outline only) g) outline the three main stages of the Calvin cycle: ? fixation of carbon dioxide by combination with ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP), a 5C compound, to yield two molecules of GP (PGA), a 3C compound ? the reduction of GP to triose phosphate (TP) involving ATP and reduced NADP ? the regeneration of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) using ATP h) describe, in outline, the conversion of Calvin cycle intermediates to carbohydrates, lipids and amino acids and their uses in the plant cell |
- #104 Separating Chlorophyll Pigments By Thin Layer Chromatography (tlc)
Chromatography is a method of separation that relies on the different solubilities of different solutes in a solvent. A mixture of chlorophyll pigments is dissolved in a solvent, and then a small spot is placed onto chromatography paper. The solvent gradually...
- # 102 The Light-dependent Reactions, Photophosphorilation
Chlorophyll molecules in photosystern I (PSI) and photosystern II (PSII) absorb light energy. The energy excites electrons, raising their energy level so that they leave the chlorophyll. The chlorophyll is said to be photo-activated. PSII contains...
- #101 Photosynthetic Pigments
Photosynthetic pigments are pigments presented in chloroplasts or photosynthetic bacteria. They capture light energy necessary for photosynthesis and convert it to chemical energy. PigmentsA pigment is any substance that absorbs light.The color...
- #100 Chloroplasts
Photosynthesis takes place inside chloroplasts. These are organelles surrounded by 2 membranes, called an envelope. Chloroplasts are found in mesophyll cells in leaves: - Palisade mesophyll cells contain most chloroplasts. - Spongy...
- #98 Photosynthesis Syllabus
13.1 Photosynthesis as an energy transfer process 13.2 Investigation of limiting factors 13.3 Adaptations for photosynthesis Photosynthesis is the energy transfer process that is the basis of much of life on Earth....
